王立辉,男,辽宁辽阳人,苏州大学教授,博导,日本东京大学博士,正高级工程师。中国民主建国会会员,地方政协委员,广州欧美同学会番禺分会副会长,广东省康复医学发展研究会理事,民建广州科信委副主任、民建广东科信委委员。历任日本东京大学特聘研究员、特聘助理教授,广东省科学院半导体研究所智能光电方向学科带头人。获广东省“珠江人才计划”引进高层次人才(青年拔尖),广东省科学院“百人计划”引进高层次人才、杰出青年、优秀青年等。电气与电子工程师学会IEEE、国际光学工程学会SPIE、美国光学学会Optica等高级会员Senior Member。
在日本东京大学留学任教期间的十余年间,师从东京大学原副校长、产学研部长、日本工程院院士石川正俊(Masatoshi Ishikawa)教授,在研究组内进行以高速视觉为核心的技术攻关,长期从事新一代超高速机器视觉和动态三维显示系统的技术研发工作。通过观察发现在毫秒级高速机器视觉系统中,传统的光学系统已经成为整个系统的瓶颈,提出利用透明液体来替代传统固体镜头,成功研发世界首台大口径全焦点高分辨率可变焦液体镜头,并将其推广至高速机器视觉及可穿戴智能眼镜等领域,其间课题曾获日本文部科学省博士生奖学金、青年基金、卓越研究员候选人,此外该成果受到日本东京电视台全球财经卫视Trend Tamago专题报道,并作为中国科技部部长和重大专项办公室主任访问东京大学时接待参观项目之一,受到了学术界及商业的密切关注。协同柯尼卡美能达公司合作研发的世界首台用于汽车辅助(自动)驾驶系统(ADAS)的三维增强现实抬头显示器,分别出展日本东京全球汽车技术博览会和德国汉诺威工业展会,备受汽车界高度关注。近年成功研发出为医学领域中的治疗计划系统的动态三维显示器,为医疗三维图像提供动态三维低延迟的人机交互环境。成果出展于世界顶级人机交互学年会(ACM CHI)、美国计算机图形学年会(ACM SIGGRAPH )和日本数字信息展会出展,并荣获美国计算机图形学会特别奖(ACM SIGGRAPH Special Prize)、日本经济产业省数字信息协会科技创新奖(Innovative Technologies )和赞助商奖(CG World Sponsor Award)、IRCE2025国际会议最佳组织奖、华创杯及深创赛等赛事奖励。以第一或通讯作者在Soft Robotics、Nano Energy、IEEE、Optics Express、Applied Optics等发表科研论文80余篇,申请授权国内外发明专利十余件,并多次受到日本东京电视台、日刊产业新闻、日本经济新闻、中国科技日报等国内外媒体报道。
研究方向凝练并融合了光、机、电、信息工程领域的科学知识。具体成果可广泛应用于,高速机器视觉,商业广播设备,高速自动对焦,全焦点摄影,高速图像追踪,三维重建,生物医疗,安防监控,动态光雕投影,虚拟/增强/混合现实技术,汽车辅助驾驶,自动驾驶等领域。
____
参考链接:
1. Dynamic Image Perception Labs: https://diplabs.wordpress.com/
2. Researchgate: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Lihui-Wang-7
3. ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3261-3728
4. Mentors: Prof. Dr. Masatoshi Ishikawa (Link, Lab Link), Prof. Dr. Hiromasa Oku (Link, Lab Link)
王立辉,辽宁辽阳人,苏州大学教授,博导,日本东京大学博士,正高级工程师,省级人才,民建会员,地方政协委员。
About/关于
人类社会的周围环境具有高速变化的动态特性,若对此变化的环境对象进行实时观测与交互,传统的采集方法和检测手段将面临很大的瓶颈。
动态图像感知(Dynamic Image Perception)名字的由来,源自日本東京大学石川正俊教授(Masatoshi Ishikawa)研究室,时任组长奥宽雅博士(Hiromasa Oku)发起的Dynamic Image Control课题组名,研究室倡导通过光、机、电、信息一体化的全局调控方式,在时间维度和空间维度上超越人类视觉感知。
Object/着眼点
研究方向围绕超高速视觉展开,以高速对焦和高速追踪为着眼点,解决以高速移动物体为采集对象时的“看不见”和“看不清”的“卡脖子”难题, 并在此基础上进一步拓展高速高清机器视觉和高速动态显示交互技术。
Originality/独创性
凝练并融合了光、机、电、信息工程领域的科学知识,以周边高速变化的动态信息为观测对象,发展新一代视觉信息感知、分析处理和显示技术。
Research and Applications/研究范围及应用场景
- 光学仪器、自适应光学设备(变焦/调焦液体透镜、智能老花眼眼镜;超高速视觉追踪)
- 先进制造、智能制造(高器视觉、机器人导航控制;柔性传感器、精密器件抓取)
- 安防、监控摄像设备(高速目标追踪、可疑目标提示)
- 新型显示、虚拟/增强/混合现实(动态光雕投影显示技术;三维车载抬头显示器;医疗手术辅助导航)
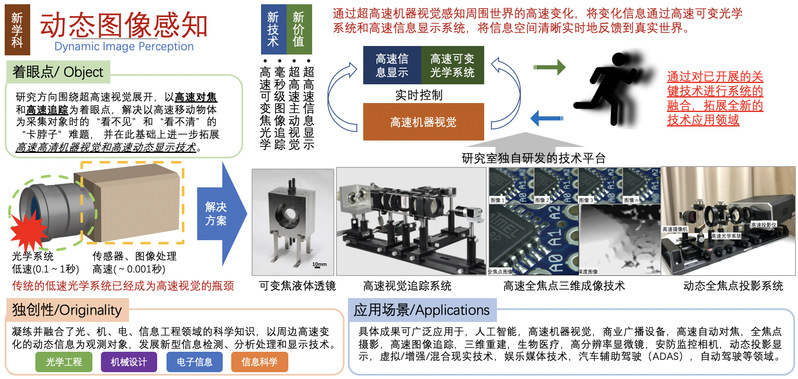
In Detail/具体展开
1 Active Vision/主动视觉
1-1 Variable Focus Lens/可变焦液体透镜
In order to change focus with traditional solid lenses, which have fixed optical properties, two or more lenses have to be jointly moved mechanically. In contrast, a variable focus lens can dynamically control its focal length by only using a single lens element. Liquid-filled variable focus lenses are based on the physical deformation of refractive surfaces, which changes their curvature.
We proposed a novel variable focus lens with a large optical aperture. The lens consists of two chambers separated by a membrane. The chambers were infused with two different liquids characterized by their similar density but different refractive indices. Thus its deformation was in the interface between the two liquids, and it acted as a refractive surface due to the difference in refractive index of these liquids. If one fluid was made to flow into and out of its chamber, while the other was locked, the lens could shift its power dynamically by means of a syringe pump.
|
|
自研可变焦距液体透镜(大口径版) A photograph of the lens prototype. | 可变焦距液体透镜的性能测试展示 Experimental view of its variable focus performance. |
|
|
可便携式可变焦距液体透镜 Waearable liquid-based tunable lens | 可便携式液体透镜(东京电视台专题报道) Waearable liquid-based tunable lens |
Reference/ 参考
Zenghong Duan, Lihui Wang*, Zhi Li, Jian Fu, Susheng Fu, Boqian Chen, Yuxun Chen, and Yong Zhao, “Dynamic performance of a membrane-based variable focus lens with a large aperture,” Appl. Opt. 62, 4609-4617 (2023)[DOI:10.1364/AO.486278]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Paraxial ray solution for liquid-filled variable focus lenses, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Volume 56, Number 12, 122501 (2017)[DOI:10.7567/JJAP.56.122501]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, An improved low-optical-power variable focus lens with a large aperture, Optics Express, Vol.22, Issue 16, pp. 19448-19456 (2014)[DOI:10.1364/OE.22.019448]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Variable-focus lens with 30 mm optical aperture based on liquid-membranes-liquid structure, Applied Physics Letters, Vol.102, 131111 (2013)[DOI:10.1063/1.4800603]
1-2 High-speed Active Visual Tracking/高速主动视觉追踪
在追踪具有高度非线性的高速随机运动目标时,传统光电主动视觉系统存在目标丢失、视觉追踪失效的问题。课题组通过搭建一套毫秒级光电主动视觉系统。采用光电云台结构、感兴趣区域提取、并行计算、高速运动目标追踪算法,实现毫秒级目标跟踪。
|
|
| 高速视觉追踪效果图. (a)目标从右至左运动过程; (b) 目标下落-碰撞地面-弹起的高动态过程。 | 球类高速运动的实时追踪,高速主动视觉系统,可以时刻保持观测对象在计算机视野中心(ball real-time tracking) |
|
|
| 6自由度实时追踪测试( test for 6-dof tracking) | 乒乓球拍6自由度实时追踪(tracking pingpang pat 6-DOF) |
Reference/参考
Jiaqi Li, Lin Li, Lihui Wang*, Lei LI, Shaoyong Li, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, Adaptive milliseconds tracking and zooming optics based on a high-speed gaze controller and liquid lenses, Optics Express, Vol.32, Issue 2, pp. 2257-2270 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/OE.512003]
Ruimin Cao, Jian Fu, Hui Yang, Lihui Wang*, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, “Robust optical axis control of monocular active gazing based on pan-tilt mirrors for high dynamic targets,” Optics Express 29, 40214-40230 (2021) [DOI: 10.1364/OE.439083]
3 High-Speed 3D & Depth Imaging/成像
A large open aperture in an optical system can capture high-resolution images but yields a shallow depth of field. In order to keep the high-resolution and enlarge the DOF at the same time, back-and-forth movement of the lens should be driven by the rack and pinion motion of a motor. However, continual forward and reverse rotation is a high-power-consumption task, because positive and negative current are used alternately to control the motor, which quickly triggers a safety stop to prevent overheating. Moreover, it is quite difficult to achieve high-speed responses in such conditions.
|
|
| 倾斜放置的芯片(传统成像方式导致局部信息清晰,局部星系模糊的典型案例) | 高速焦点扫描成像方式,短时间内采集12张不同景深图像(左下),通过自研图像处理算法,实时生成全焦点图(右上) |
|
|
| 眼底模型(大景深物体) | 实时对焦点扩展景深成像(shape from focus) |
Reference/参考
Huayu Cheng, Lihui Wang*, Satoshi Tabata, Yuan He, Yan Hu, Jiang Liu and Zhiwei Mou, High-speed all-in-focus 3D imaging method based on the liquid lens focus scanning, Applied Optics, Vol.63, Issue 21, pp. 5602-5610 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/AO.523864]
Lihui Wang, Jianjiang Cui, Satoshi Tabata, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Low-cost, readily available 3D microscopy imaging system with variable focus spinner, Optics Express, Vol.26, Issue 23, pp. 30576-30587 (2018).[DOI:10.1364/OE.26.030576]
4 High-Speed 3D Projection Mapping/显示
Projection mapping (PM) is attractive as a fundamental technology for the advancement of various subjects, such as media art, entertainment, and augmented reality. However, conventional projectors have a shallow depth of field (DOF); therefore, sharp images are only visible in the limited depth range. In the case of dynamic projection mapping (DPM), which can project images on the surface of the moving objects, the shallow DOF limits the permissible motion of the object, because the projected images become blurred when the object is outside the DOF.
Our laboratories have developed a high-speed focal tracking projection system, which includes the technologies of high-speed vision, high-speed projector, and high-speed variable focus optics. In this system, the variation of the object’s distance and posture was captured using the high-speed vision technology that served as immediate feedback to the liquid lens and high-speed projector. As a result, the focal distance is compensated, and the projected images are updated in real-time to fit the moving object. Therefore, a well-focused image projection was achieved even when the motion involved large depth range movement.
This system could ensure that the projected images were sharp and clear at variable distances, while the object was moving dynamically in a large three-dimensional area. Hence, this approach can be effectively applied to applications such as Volume Slicing Display. Furthermore, it can turn any physical surface into an interactive display, and enable the manipulation of their appearance to provide detailed information. Our system provides the essential technology for expanding such applications.
|
|
| Prototype of projection tracking system using a liquid lens. (Ver.7) (2018-) | Prototype of projection tracking system using a liquid lens. (Ver.2) (2019-) |
|
| Volume Slicing Display: change images based on the distance. |
|
|
|
提案系统能实时保持投影对焦清晰(左侧图为本系统)our projector is always in focus (left) | 即使投影对象时刻旋转,投影信息能根据旋转反馈调整/Target rotationcan be detected self adjust projection | 医疗用三维数据信息能够在三维空间内做高清切片投影展示/ 3D CT data can be projected and shown with slicing display |
本技术与2019年11月19日获得日本经济产业省数字信息科技创新奖、美国计算机图形学会特等奖、日本CGWorld赞助商奖三项奖励。此次授奖也是日本数字信息展,首次将三个奖项同时授予同一项技术。
The following three awards were given to the project “High-speed focal tracking projection system based on liquid lens”.
ACM SIGGRAPH Special Prize, (Association for Computing Machinery)
Innovative Technologies 2019, (Digital Content Association of Japan)
Innovative Technologies 2019, Sponsor Award (CGWORLD) 2019, (Digital Content Association of Japan)
Reference/ 参考
Lihui Wang*, Satoshi Tabata, Hongjin Xu, Yunpu Hu, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic depth-of-field projection mapping method based on a variable focus lens and visual feedback, Optics Express, 31(3), pp. 3945-3953 (2023) [DOI:10.1364/OE.478416]
Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Satoshi Tabata, Yunpu Hu, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: High-Speed Focal Tracking Projection Based on Liquid Lens, ACM SIGGRAPH 2020 Emerging Technologies (SIGGRAPH ’20) (Virtual Event, USA, 2020.8.24-28) [DOI: 10.1145/3388534.3408333]
Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Yunpu Hu, Satoshi Tabata, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic Depth-of-Field Projection for 3D Projection Mapping, ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI’19) (Glasgow, Scotland, UK. 2019.05.05-09) [DOI: 10.1145/3290607.3313246]
5 3D Augmented Reality Head-Up-Display / 三维增强现实车载抬头显示器
Head-Up-Display (HUD) enables a driver to view information with his head positioned “up” and looking forward, instead of angled down looking at lower instruments. By adding the Augmented Reality technology, targets, like people and cars, can be marked to alarm to the drivers to avoid the potential accidents.
Traditional 2D AR HUD projects information messages at a certain distance away from the driver. It asks a driver to observe the projection along the optical axis at a certain point. When the driver moves his head, a miss-matching projection occurs between the projected data and the target in the real world.
In this 3D AR HUD technology, a 3D virtual display can be projected in front of the driver. AR messages will be dynamically projected according to the 3D locations of the targets. In our 3D HUD, a virtual display is projected into a three-dimensional world, so there will be no mismatch when the driver moves.
The following demos were recorded by two cameras, which were placed at different places. When the camera was placed along the optical axis, 2D and 3D markers were all perfectly matched. When the camera was placed at an angle to the optical axis, a mismatch was found in 2D HUD, but 3D HUD was still well matched.
This work was conducted by a collaborate research project with Ishikawa Laboratory and Konica Minolta Inc..
|
|
|
| A photo of 2D HUD projection. All the 2D HUD markers were projected at a certain distance. | A photo of 3D HUD projection. 3D HUD markers were projected at different distance. This photo were token when it focused at close. | A photo of 3D HUD projection. 3D HUD markers were projected at different distance. This photo were token when it focused at far. |
6 Smart Actuator and sensor/软体驱动器和传感器
力触觉感知和交互作为人-机交互的主要方式之一,其通常需要人工设备具备良好的柔性触觉感知能力。为丰富人工设备所能感知的触觉信息,基于混合感知机理的触觉传感器近年来受到了广泛关注。然而,对于可穿戴或柔性人工设备而言,开发具有简单结构、易制备、成本低、功耗低、易于维护和集成的触觉传感器仍然是一项艰巨挑战。
|
|
| 自研基于液体透镜的柔性触觉感知器,抓取柔性物体 | 基于力反馈控制实现对超软物体的无损抓取 |
Reference/参考
Hui Yang, Tianzhao Bu*, Wenbo Liu, Jiaqi Liu, Yunzhi Ling, Meixia Wu, Weirui Liu, Changan Wang*, Xifeng Gao*, Lihui Wang*, A novel triboelectric-optical hybrid tactile sensor for human-machine tactile interaction, Nano Energy, 125, pp. 109592 (2024) [DOI:10.1016/j.nanoen.2024.109592] (IF=17.6)
Ronghua Hu, Hui Yang, Lihui Wang*, and Longfei Fan, Flexible optical tactile sensor based on a liquid-membrane lens structure, Applied Optics, 62(26), 6952-6960 (2023) [DOI:10.1364/AO.496741](IF=1.905)
Hui Yang, Jiaqi Liu, Wenbo Liu, Weirui Liu, Zilong Deng, Yunzhi Ling, Changan Wang, Meixia Wu, Lihui Wang*, and Li Wen*, Compliant Grasping Control for a Tactile Self-Sensing Soft Gripper, Soft Robotics, (2023) [DOI:10.1089/soro.2022.0221] (IF=7.784)
Media and others (媒体报道等)
1. Dynamic Projection Mapping(动态光雕投影)
1) ITmedia News. 液体レンズを用いた高速焦点追従投影システム[https://dip-labs.com/news/20210128-01/] (2021.01) (日本語)
译:ITmedia News,基于液体的动态光雕投影系统。
2) 中国科技网/科技日报. “液体透镜带来光学镜头革命” [http://www.stdaily.com/index/kejixinwen/2019-11/21/content_817911.shtml?from=singlemessage](2019.11) (in Chinese)
3) 日刊工業新聞. “動く物体に絵を投影できるプロジェクション技術、どんな用途に使う”[https://newswitch.jp/p/20672?fbclid=IwAR3MP-srPICwf7SsFN333tQQ-9pA-Jddmu1eq8ElD61jKqIMw6nge9yeGrU] (2020.01) (in Japanese)
译:日刊工业新闻。可在移动物体表面绘画的光雕投影技术,潜在用途是?
2. Variable Focus Lens(可变焦液体镜头)
1) テレビ東京ワールドビジネスサテライトトレンドたまご [オートフォーカスの老眼鏡!?] [https://txbiz.tv-tokyo.co.jp/wbs/trend_tamago/post_124134/] (2017.01) (in Japanese)
译:东京电视台,全球财经卫视Trend Tamago专题,自动对焦老花眼眼镜!
3. 3D AR Head-Up-Display for ADAS Automotive(车载三维抬头显示器)
1) Konica Minolta Release. “Konica Minolta Develops the World’s First* Automotive 3D Augmented Reality Head-up Display” [https://www.konicaminolta.com/newsroom/2017/0227_01_01.html]. (2017.02)
译:柯尼卡美能达,世界首发车载三维增强现实抬头显示器
2) コニカミノルタニュースリリース.“コニカミノルタ 世界初*の車載用3D 拡張現実ヘッドアップディスプレイを開発” [https://www.konicaminolta.com/jp-ja/newsroom/2017/0113_01_01.html]. (2017.01) (in Japanese)
译:柯尼卡美能达,世界首发车载三维增强现实抬头显示器
3) 日本経済新聞. “車載用3D拡張現実ヘッドアップディスプレーを開発” [https://www.nikkei.com/article/DGXLRSP433224_T10C17A1000000/].(2017.01) (in Japanese)
译:日本经济新闻,车载三维增强现实抬头显示器
更加详细的研究信息可参考:diplabs.wordpress.com
欢迎对光机电一体化、液态透镜、高速视觉追踪、动态投影/AR/VR交互等方向感兴趣的老师同学联系!
长期同東京大学、東京理科大学、東京科学大学、群馬大学、香港理工大学、香港城市大学等高校合作!
欢迎以下专业代码的同学联系,名额充足,谢谢关注(^_^)v.
》请发电邮到wanglihui@suda.edu.cn,标题(x级-x大学-x专业--姓名),并附个人简历,谢谢。
》为保证公平录取,准备推免和考研复试中的同学们,待明确录取资格后再联系,祝你们好运!
081200 计算机科学与技术(学硕)
085410 人工智能(专硕)
080200 机械工程(学硕)
085501 机械工程(专硕)
Team/团队
| 副教授/Assoc. Prof. | 胡衍/Yan Hu(兼) |
| 讲师/Lecture | 李璐/Lu Li |
| 工程师/Engineer | 彭翠玲 博士/Dr. Cuiling Peng(兼); 胡书赫/Shuhe Hu(兼) |
| 博士生/Ph.d Student | 黄双江/Shuangjiang Huang(高速视觉及姿态检测) 段增鸿/Zenghong Duan(可变焦镜头及运动控制) 孙浩楠/Haonan Sun(高速机器视觉感知) |
| 硕士生/M.S. Student | 桂旭/Xu Gui(高速视觉追踪及位姿检测) |
王迦羽/Jiayu Wang(高速视觉及人机交互) 彭贵远/Guiyuan Peng(高速视觉追踪) 沈寅驰/Yinchi Shen(可变焦镜头开发) 张超洋/Chaoyang Zhang(高速视觉检测) | |
高莉婷/Liting Gao 蔡华宏/Huahong Cai 孙浩/Hao Sun 李文致/Wenzhi Li 何瑞昭/Ruizhao He | |
| 本科生/Bachelor Student | ... ... |
| 访问生/Visit Student | 张峻豪/Junhao Zhang |
教师室:未来科创中心513
学生室:未来科创中心611
实验室:未来科创中心705-1-2、1201-1-5
Alumni/毕业生
| 科研骨干/Staff | ||
| 2020.12-2024.03 | 杨辉/Hui Yang | 高校教师 |
| 2020.05-2021.12 | 付健/Jian Fu | 高校教师 |
| 2019.10-2021.12 | 曹瑞珉/Ruimin Cao | 高企就职 |
| 学生/ Student | ||
| 研究生/Master | ||
| 2023.09-2025.06 | 黄宇韬/Yutao Huang | 海外留学读博(*校优秀毕业论文) |
| 陈显华/Xianhua Chen | 上市公司就职 | |
| 许凯涵/Kaihan Xu | 高校教师 | |
| 2022.09-2024.06 | 张潇/Xiao Zhang | 海外留学读博 |
| 程铧钰/Huayu Cheng | 高校教师 | |
| 黎嘉祺/Jiaqi Li | 海外留学读博 | |
| 唐山根/Shangen Tang | 高校教师 | |
| 胡荣桦/Ronghua Hu | 高企就职 | |
| 2021.09-2023.06 | 宋丰年/Fengnian Song | 高企就职 |
| 本科生/Bachelor | ||
| 2024.12-2025.06 | 周锦枝/Jinzhi Zhou | 攻读硕士 |
| 郑胜楠/Shengnan Zheng | 攻读硕士 | |
| 罗仕权/Shiquan Luo | 企业就职 | |
| 实习生/Intern | ||
| 2022.07-2022.08 | 钦壮飞/Zhuangfei Qin | 海外留学 |
| 2021.08-2021.12 | 李嘉驹/Jiaju Li | 企业就职 |
| 林文裕/Wenyu Lin | 企业就职 | |
| 本科生成长陪伴 | ||
| 2024.09-2025.06 | 黄广维(导生,22级机械电子) | |
| 团队43 | 胡泽嘉、吴胤霖、潘浩宇、何玖 鹏(学生,24级机械电子) |
Album/相册
2025-09-20 |
|
2024-12-11 |
2024-09-23 |
2024-04-10 |
1 Active Vision/主动视觉
1-1 Variable Focus Lens/可变焦液体透镜
In order to change focus with traditional solid lenses, which have fixed optical properties, two or more lenses have to be jointly moved mechanically. In contrast, a variable focus lens can dynamically control its focal length by only using a single lens element. Liquid-filled variable focus lenses are based on the physical deformation of refractive surfaces, which changes their curvature.
We proposed a novel variable focus lens with a large optical aperture. The lens consists of two chambers separated by a membrane. The chambers were infused with two different liquids characterized by their similar density but different refractive indices. Thus its deformation was in the interface between the two liquids, and it acted as a refractive surface due to the difference in refractive index of these liquids. If one fluid was made to flow into and out of its chamber, while the other was locked, the lens could shift its power dynamically by means of a syringe pump.
|
|
A cross-sectional view of the lens system. | A photograph of the lens prototype. |
Reference/ 参考
Zenghong Duan, Lihui Wang*, Zhi Li, Jian Fu, Susheng Fu, Boqian Chen, Yuxun Chen, and Yong Zhao, “Dynamic performance of a membrane-based variable focus lens with a large aperture,” Appl. Opt. 62, 4609-4617 (2023)[DOI:10.1364/AO.486278]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Paraxial ray solution for liquid-filled variable focus lenses, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Volume 56, Number 12, 122501 (2017)[DOI:10.7567/JJAP.56.122501]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, An improved low-optical-power variable focus lens with a large aperture, Optics Express, Vol.22, Issue 16, pp. 19448-19456 (2014)[DOI:10.1364/OE.22.019448]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Variable-focus lens with 30 mm optical aperture based on liquid-membranes-liquid structure, Applied Physics Letters, Vol.102, 131111 (2013)[DOI:10.1063/1.4800603]
1-2 Active Visual Tracking/主动视觉追踪
在追踪具有高度非线性轨迹的高速随机运动目标时,传统光电主动视觉系统存在目标丢失、视觉追踪失效的问题。课题组通过搭建了一套毫秒级光电主动视觉系统。采用光电云台结构、感兴趣区域提取、并行计算、高速运动目标追踪算法,实现响应时间≤2ms毫秒级的目标跟踪。
|
|
| 高速视觉追踪效果图. (a)目标从右至左运动过程; (b) 目标下落-碰撞地面-弹起的高动态过程。 | 视频. 基于毫秒级光电主动视觉系统的高动态目标追踪实验 |
Reference/参考
Jiaqi Li, Lin Li, Lihui Wang*, Lei LI, Shaoyong Li, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, Adaptive milliseconds tracking and zooming optics based on a high-speed gaze controller and liquid lenses, Optics Express, Vol.32, Issue 2, pp. 2257-2270 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/OE.512003]
Ruimin Cao, Jian Fu, Hui Yang, Lihui Wang*, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, “Robust optical axis control of monocular active gazing based on pan-tilt mirrors for high dynamic targets,” Optics Express 29, 40214-40230 (2021) [DOI: 10.1364/OE.439083]
3 High-Speed 3D & Depth Imaging/成像
A large open aperture in an optical system can capture high-resolution images but yields a shallow depth of field. In order to keep the high-resolution and enlarge the DOF at the same time, back-and-forth movement of the lens should be driven by the rack and pinion motion of a motor.
However, continual forward and reverse rotation is a high-power-consumption task, because positive and negative current are used alternately to control the motor, which quickly triggers a safety stop to prevent overheating. Moreover, it is quite difficult to achieve high-speed responses in such conditions.
|
Images obtained by changing the plate thickness from 0 mm to 11 mm. (a) Raw image sequence. (b) Images obtained after rescaling, phase correction, and Laplacian edge detection. (c) All-in-focus sharp image generated by merging the in-focus pixels. (d) Depth map produced by using the index numbers of the images, which contained depth information. |
Reference/参考
Huayu Cheng, Lihui Wang*, Yuan He, , High-speed all-in-focus 3D imaging technology based on the liquid lens focus scanning, SPIE/COS Photonics Asia (Beijing, 2023.10.16) / (Oral 12767-11) doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2686779
Lihui Wang, Jianjiang Cui, Satoshi Tabata, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Low-cost, readily available 3D microscopy imaging system with variable focus spinner, Optics Express, Vol.26, Issue 23, pp. 30576-30587 (2018).[DOI:10.1364/OE.26.030576]
4 High-Speed 3D Projection Mapping/显示
Projection mapping (PM) is attractive as a fundamental technology for the advancement of various subjects, such as media art, entertainment, and augmented reality. However, conventional projectors have a shallow depth of field (DOF); therefore, sharp images are only visible in the limited depth range. In the case of dynamic projection mapping (DPM), which can project images on the surface of the moving objects, the shallow DOF limits the permissible motion of the object, because the projected images become blurred when the object is outside the DOF.
Our laboratories have developed a high-speed focal tracking projection system, which includes the technologies of high-speed vision, high-speed projector, and high-speed variable focus optics. In this system, the variation of the object’s distance and posture was captured using the high-speed vision technology that served as immediate feedback to the liquid lens and high-speed projector. As a result, the focal distance is compensated, and the projected images are updated in real-time to fit the moving object. Therefore, a well-focused image projection was achieved even when the motion involved large depth range movement.
This system could ensure that the projected images were sharp and clear at variable distances, while the object was moving dynamically in a large three-dimensional area. Hence, this approach can be effectively applied to applications such as Volume Slicing Display. Furthermore, it can turn any physical surface into an interactive display, and enable the manipulation of their appearance to provide detailed information. Our system provides the essential technology for expanding such applications.
|
|
| Prototype of projection tracking system using a liquid lens. (Ver.7) (2018-) | Prototype of projection tracking system using a liquid lens. (Ver.2) (2019-) |
|
| System configuration. |
|
| In-focus projection in the large depth range. |
|
| Volume Slicing Display: change images based on the distance. |
The following three awards were given to the project “High-speed focal tracking projection system based on liquid lens”.
ACM SIGGRAPH Special Prize, (Association for Computing Machinery)
Innovative Technologies 2019, (Digital Content Association of Japan)
Innovative Technologies 2019, Sponsor Award (CGWORLD) 2019, (Digital Content Association of Japan)
Reference/ 参考
Lihui Wang*, Satoshi Tabata, Hongjin Xu, Yunpu Hu, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic depth-of-field projection mapping method based on a variable focus lens and visual feedback, Optics Express, 31(3), pp. 3945-3953 (2023) [DOI:10.1364/OE.478416]
Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Satoshi Tabata, Yunpu Hu, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: High-Speed Focal Tracking Projection Based on Liquid Lens, ACM SIGGRAPH 2020 Emerging Technologies (SIGGRAPH ’20) (Virtual Event, USA, 2020.8.24-28) [DOI: 10.1145/3388534.3408333]
Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Yunpu Hu, Satoshi Tabata, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic Depth-of-Field Projection for 3D Projection Mapping, ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI’19) (Glasgow, Scotland, UK. 2019.05.05-09) [DOI: 10.1145/3290607.3313246]
Lihui Wang, Yunpu Hu, Hongjin Xu, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic focal tracker display, SPIE Photonics West 2019 (San Francisco, California, USA. 2019.02.07)/ (Oral Session) [DOI: 10.1117/12.2506958]
5 3D Augmented Reality Head-Up-Display / 三维增强现实车载抬头显示器
Head-Up-Display (HUD) enables a driver to view information with his head positioned “up” and looking forward, instead of angled down looking at lower instruments. By adding the Augmented Reality technology, targets, like people and cars, can be marked to alarm to the drivers to avoid the potential accidents.
Traditional 2D AR HUD projects information messages at a certain distance away from the driver. It asks a driver to observe the projection along the optical axis at a certain point. When the driver moves his head, a miss-matching projection occurs between the projected data and the target in the real world.
In this 3D AR HUD technology, a 3D virtual display can be projected in front of the driver. AR messages will be dynamically projected according to the 3D locations of the targets. In our 3D HUD, a virtual display is projected into a three-dimensional world, so there will be no mismatch when the driver moves.
The following demos were recorded by two cameras, which were placed at different places. When the camera was placed along the optical axis, 2D and 3D markers were all perfectly matched. When the camera was placed at an angle to the optical axis, a mismatch was found in 2D HUD, but 3D HUD was still well matched.
This work was conducted by a collaborate research project with Ishikawa Laboratory and Konica Minolta Inc..
|
|
|
| A photo of 2D HUD projection. All the 2D HUD markers were projected at a certain distance. | A photo of 3D HUD projection. 3D HUD markers were projected at different distance. This photo were token when it focused at close. | A photo of 3D HUD projection. 3D HUD markers were projected at different distance. This photo were token when it focused at far. |
6 Smart Actuator and sensor/软体驱动器和传感器
触觉感知和交互作为人-机交互的主要方式之一,其通常需要人工设备具备良好的触觉感知能力。为丰富人工设备所能感知的触觉信息,基于混合感知机理的触觉传感器近年来受到了广泛关注。然而,对于可穿戴或柔性人工设备而言,开发具有简单结构、易制备、成本低、功耗低、易于维护和集成的触觉传感器仍然是一项艰巨挑战。
在此背景下研究团队提出了一种新型的摩擦电-光电混合触觉传感器,其采用模块化分体式结构,包括两个单元:基于单电极摩擦电纳米发电机设计的摩擦电单元,用于接收外部触觉刺激;以及基于可变焦液体透镜结构的光电单元,用于将触觉刺激转化为光电信号。两个单元均采用单腔体结构,可轻松实现对单元零部件的拆卸与更换。此外,摩擦电单元可根据其输出信号控制光电单元内部所嵌光源的开/关行为,从而降低传感单元功耗,提高触觉响应速度。光电单元具有优越的电磁干扰抗性,使得传感器能够准确、定量地感知接触力。通过开展感知性能测试实验,表现出响应时间短(~9 ms)、输出线性度高(R2≈0.9952)、耐久性和稳定性好等特点。基于上述特点,通过进一步设计-开展文字键入、图形绘制、音乐演奏等触觉交互实验,展示了本传感器在触觉交互任务中的实用性,进而说明其在人-机交互设备领域中具有广阔的应用前景。
|
| 如图,(左上)摩擦电-光电混合触觉传感器结构图,(右上)传感器得动作机理,(左下、右下)面向摩斯电码、迷宫游戏和绘图操作功能,传感器按钮的人机交互配置方案。 |
Reference/参考
Hui Yang, Tianzhao Bu*, Wenbo Liu, Jiaqi Liu, Yunzhi Ling, Meixia Wu, Weirui Liu, Changan Wang*, Xifeng Gao*, Lihui Wang*, A novel triboelectric-optical hybrid tactile sensor for human-machine tactile interaction, Nano Energy, 125, pp. 109592 (2024) [DOI:10.1016/j.nanoen.2024.109592] (IF=17.6)
Ronghua Hu, Hui Yang, Lihui Wang*, and Longfei Fan, Flexible optical tactile sensor based on a liquid-membrane lens structure, Applied Optics, 62(26), 6952-6960 (2023) [DOI:10.1364/AO.496741](IF=1.905)
Hui Yang, Jiaqi Liu, Wenbo Liu, Weirui Liu, Zilong Deng, Yunzhi Ling, Changan Wang, Meixia Wu, Lihui Wang*, and Li Wen*, Compliant Grasping Control for a Tactile Self-Sensing Soft Gripper, Soft Robotics, (2023) [DOI:10.1089/soro.2022.0221] (IF=7.784)
| 博士生/Ph.d Student | 黄双江/Shuangjiang Huang |
| 硕士生/M.S. Student | 张潇/Xiao Zhang;程铧钰/Huayu Cheng 黎嘉祺/Jiaqi Li;唐山根/Shangen Tang;胡荣桦/Ronghua Hu |
| 许凯涵/ Kaihan Xu;陈显华/Xianhua Chen;黄宇韬/Yutao Huang | |
| 桂旭/Xu Gui;陈维耀/Weiyao Chen |
Alumni/毕业生
| 科研骨干/Staff | ||
| 2020.12-2024.03 | 杨辉/Hui Yang | 某高等学校教师 |
| 2020.05-2021.12 | 付健/Jian Fu | 某高等学校教师 |
| 2019.10-2021.12 | 曹瑞珉/Ruimin Cao | 某大手通讯终端企业 |
| 学生/ Student | ||
| 2021.09-2023.06 | 宋丰年/Fengnian Song | 某专精特新“小巨人”公司 |
| 实习生/Intern | ||
| 2022.07-2022.08 | 钦壮飞/Zhuangfei Qin | |
| 2021.08-2021.12 | 李嘉驹/Jiaju Li | |
| 2021.08-2021.12 | 林文裕/Wenyu Lin |
1、自动控制原理
2、机器视觉
3、传感器与检测技术
》相关资料下载
| 自动控制原理 | 机器视觉 | 传感器与检测技术 |
 |  |
|
Publications and patents
仅列一作/通讯中代表性论文,https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3261-3728
- Journals (*corresponding author)
Shuangjiang Huang, Fengnian Song, Lihui Wang*, Yutao Huang, Yuan He, Shi Bai, Tao Chen, Masatoshi Ishikawa, High-speed active vision pose perception and tracking method based on Pan-Tilt mirrors for 6-DOF dynamic projection mapping, Optics and Lasers in Engineering, Volume 188, 2025, 108888,[DOI:10.1016/j.optlaseng.2025.108888]
Xianhua Chen, Lihui Wang*, Jianhua Tang, Shuangjiang Huang, Real-time reconstruction of multi-person 3D human pose with perspective transformation matching based on multi-view, Journal of Electronic Imaging, Vol.34(2), pp.023023, (2025) [10.1117/1.JEI.34.2.023023]
Yutao Huang, Lihui Wang*, Shuangjiang Huang, Longfei Fan, Tao Chen, 42 mm large aperture variable-focus lens based on the liquid-membrane-liquid structure, Optics Express, 32(25), pp. 44706-44720 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/OE.539941]
Hui Yang, Tianzhao Bu*, Wenbo Liu, Jiaqi Liu, Yunzhi Ling, Meixia Wu, Weirui Liu, Changan Wang*, Xifeng Gao*, Lihui Wang*, A novel triboelectric-optical hybrid tactile sensor for human-machine tactile interaction, Nano Energy, 125, pp. 109592 (2024) [DOI:10.1016/j.nanoen.2024.109592]
Shuangjiang Huang, Lihui Wang*, Yutao Huang, Yuan He, Shi Bai, Measurement method of virtual image distance for head-mounted display based on a variable-focus liquid lens, Applied Optics, Vol.63, Issue 15, pp. 4175-4181 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/AO.524353]
Huayu Cheng, Lihui Wang*, Satoshi Tabata, Yuan He, Yan Hu, Jiang Liu and Zhiwei Mou, High-speed all-in-focus 3D imaging method based on the liquid lens focus scanning, Applied Optics, Vol.63, Issue 21, pp. 5602-5610 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/AO.523864]
Xiao Zhang, Lihui Wang*, Zhiwei Mou, Yiqi Cao, Yuan He, High-speed eye-tracking based on a synchronized imaging mechanism by dual-ring infrared lighting source, Applied Optics, Vol.63, Issue 16, pp. 4293-4302 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/AO.521840]
Jiaqi Li, Lin Li, Lihui Wang*, Lei Li, Shaoyong Li, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, Adaptive milliseconds tracking and zooming optics based on a high-speed gaze controller and liquid lenses, Optics Express, Vol.32, Issue 2, pp. 2257-2270 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/OE.512003]
Shangen Tang, Lihui Wang*, Fengnian Song, and Shaoyong Li, Dynamic projection mapping for non-planar objects with a variable focus lens and visual feedback, Journal of the Optical Society of America A, Vol. 41, Issue 3, pp. 468-475 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/JOSAA.514287]
王立輝,田畑智志,徐鴻金,胡云普,渡辺義浩,石川正俊:液体レンズを用いた高速焦点追従投影システム, 光学, 53巻, 第6号, p.234 (2024)
Lin Li, Na Xie, Jia-Qi Li, Jing-Yi Fu, Shu-Bin Liu, Li-Hui Wang, Yu-Hai Li, Lei Li, Optofluidic zoom system with increased field of view and less chromatic aberration, Optics Express, Vol.31, Issue 15, pp. 25117-25127 (2023) [DOI:10.1364/OE.498096]
Hui Yang, Jiaqi Liu, Wenbo Liu, Weirui Liu, Zilong Deng, Yunzhi Ling, Changan Wang, Meixia Wu, Lihui Wang* and Li Wen*, Compliant Grasping Control for a Tactile Self-Sensing Soft Gripper, Soft Robotics, (2023) [DOI:10.1089/soro.2022.0221]
Ronghua Hu, Hui Yang, Lihui Wang*, and Longfei Fan, Flexible optical tactile sensor based on a liquid-membrane lens structure, Applied Optics, 62(26), 6952-6960 (2023) [DOI:10.1364/AO.496741
Zenghong Duan, Lihui Wang*, Zhi Li, Jian Fu, Susheng Fu, Boqian Chen, Yuxun Chen, and Yong Zhao, “Dynamic performance of a membrane-based variable focus lens with a large aperture,” Appl. Opt. 62, 4609-4617 (2023)[DOI:10.1364/AO.486278]
Lihui Wang*, Satoshi Tabata, Hongjin Xu, Yunpu Hu, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic depth-of-field projection mapping method based on a variable focus lens and visual feedback, Optics Express, 31(3), pp. 3945-3953 (2023) [DOI:10.1364/OE.478416]
Hao Xu, Satoshi Tabata, Haowen Liang*, Lihui Wang*, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: Accurate Measurement of Virtual Image Distance for Near-Eye Displays Based on Auto-Focusing, Applied Optics, 61, 9093-9098 (2022) [DOI: 10.1364/AO.472931]
Yao Li, Lei Min, John H. Xin, Lihui Wang, Qinghua Wu, Longfei Fan*, Feng Gan, and Hui Yu, High-performance Fibrous Artificial Muscle Based on Reversible Shape Memory UHMWPE, Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 20, 7-17, 2022 [DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.07.045]
Ruimin Cao, Hui Yang, Jianjiang Cui, Lina Hao, and Lihui Wang*, Situation Representation and Strategic Reasoning Method of Hybrid Game System Based on Modified Hybrid Stochastic Timed Petri Net, IEEE Systems Journal, 1-11, 2022 [DOI: 10.1109/JSYST.2022.3189547]
Hui Yang, Wenbo Liu, Jiaqi Liu, Yunzhi Ling, Meixia Wu, Weirui Liu, Lihui Wang*, Liquid Lens-based Optical Tactile Sensor with a Touch-Sensing Separable Structure, Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2200674 (2022) (accepted)
Yuping Wang, Senwei Xie, Lihui Wang*, Hongjin Xu, Satoshi Tabata, Masatoshi Ishikawa. ARSlice: Head-Mounted Display Augmented with Dynamic Tracking and Projection, Journal of Computer Science and Technology 37(3), 666-679 (2022) [DOI: 10.1007/s11390-022-2173-y]
Hui Yang, Jian Fu, Ruimin Cao, Jiaqi Liu and Lihui Wang*, “A Liquid Lens-based Optical Sensor for Tactile Sensing,” Smart Materials and Structures 31(3), 035011 (2022) [DOI: 10.1088/1361-665X/ac4d64]
Ruimin Cao, Jian Fu, Hui Yang, Lihui Wang*, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, “Robust optical axis control of monocular active gazing based on pan-tilt mirrors for high dynamic targets,” Optics Express 29, 40214-40230 (2021) [DOI: 10.1364/OE.439083]
Hongjin Xu, Lihui Wang*, Satoshi Tabata, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, Extended depth-of-field projection method using a high-speed projector with a synchronized oscillating variable-focus lens, Applied Optics, 60(13), pp. 3917-3924 (2021) [DOI: 10.1364/AO.419470]
Zhangxu Pan, Chan Guo, Xianchi Wang, Jiucheng Liu, Ruimin Cao, Yanfen Gong, Jiantai Wang, Ningyang Liu, Zhitao Chen, Lihui Wang, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Zheng Gong, Wafer-Scale Micro-LEDs Transferred onto an Adhesive Film for Planar and Flexible Displays, Advanced Materials Technologies, 2000549 (2020)[DOI: 10.1002/admt.202000549]
Chen Zhang, Jianjiang Cui, Lihui Wang, Hao Wang, Multi-focus Image Fusion and Depth Reconstruction, Journal of Electronic Imaging, 29(3), 033016 (2020) [DOI: 10.1117/1.JEI.29.3.033016]
Ruimin Cao, Lihui Wang, Lina Hao, Wenlin Chen, Junxiang Deng, A Decision-making Framework of Hybrid System based on Modified Hybrid Stochastic Timed Petri Net and Deep Learning, IEEE Systems Journal, 2020. [DOI: 10.1109/JSYST.2020.2983044].
Lihui Wang, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic response of elastomer-based liquid-filled variable focus lens, Sensors, Vol.19, No.21, Article No.4624 pp:1-13 (2019) [DOI:10.3390/s19214624]
Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Solar energy-actuated back and forth optical mechanism, Applied Optics, Vol.58, No.15, pp. E7-E11 (2019) [DOI:10.1364/AO.58.0000E7]
Lihui Wang, Jianjiang Cui, Satoshi Tabata, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Low-cost, readily available 3D microscopy imaging system with variable focus spinner, Optics Express, Vol.26, Issue 23, pp. 30576-30587 (2018).[DOI:10.1364/OE.26.030576]
Lihui Wang, Tomohiko Hayakawa, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dielectric-elastomer-based fabrication method for varifocal microlens array, Optics Express, Vol.25, Issue 25, pp. 31708-31717 (2017)[DOI:10.1364/OE.25.031708]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Paraxial ray solution for liquid-filled variable focus lenses, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Volume 56, Number 12, 122501 (2017)[DOI:10.7567/JJAP.56.122501]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, An improved low-optical-power variable focus lens with a large aperture, Optics Express, Vol.22, Issue 16, pp. 19448-19456 (2014)[DOI:10.1364/OE.22.019448]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Variable-focus lens with 30 mm optical aperture based on liquid-membranes-liquid structure, Applied Physics Letters, Vol.102, 131111 (2013)[DOI:10.1063/1.4800603]
崔建江, 王立辉, 陈⼤力, 潘峰, 基于近红外图像质量量评价的静脉图像采集系统, 东北大学学报(自然科学版),2009,30(8):1099-1102.
- Invited Speech
30. Lihui Wang, Research on a High-speed Active Vision Pose Perception Method for Dynamic Projection Mapping, 6th International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Control Engineering (IRCE2023) (Jilin, 2023.08.04) / Invited
31. Lihui Wang, Dynamic Performance of the membrane-based variable focus lens, 12th Applied Optics and Photonics China (AOPC2023) (Beijing, 2023.07.26) / Invited
32. Lihui Wang, Dynamic Projection Mapping with High Speed Vision and a Variable Focus Lens, 2022 Optica Applied Industrial Optics (Ireland, 2022.07.25-27) / Invited
33. Lihui Wang, The 6th International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Control Engineering (IRCE 2023), (Tianjin, 2022.09.25)/ Invited
34. Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Satoshi Tabata, Yunpu Hu, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa. High-Speed Focal Tracking Projection Based on Liquid Lens. In Special Interest Group on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques Conference Emerging Technologies (SIGGRAPH ’20 Emerging Technologies), 2020.08.17, Virtual Event, USA. [DOI: 10.1145/3388534.3408333]
35. Lihui Wang, A large aperture variable focus lens and its application on the next generation of clinical optics, 2015 EMN Optoelectronics Meeting (Beijing, 2015.04.26) / Invited, pp. 195-196
- International Conference and Proceedings
36. Kaihan Xu, Lihui Wang*, Fuqin Deng and Jianle Chen, Research on an Occlusion-Resistant Human Pose Estimation Algorithm, 7th International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Control Engineering (IRCE2024) (Xi’an, 2024.08.09)
37. Xianhua Chen, Lihui Wang*, Qiongyao Wang and Jianhua Tang, 3D Human Pose Estimation and Tracking based on FeedbackMechanism, 7th International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Control Engineering (IRCE2024) (Xi’an, 2024.08.09)
38. Xiao Zhang, Lihui Wang*, Yuan He, Zhiwei Mou, Yiqi Cao, Milliseconds eye-tracking mechanism for high precision medical device, 21st IEEE MDBS-BHE’ Symposium 2023 (HongKong, 2023.12.20) / (Oral)
39. Huayu Cheng, Lihui Wang*, Satoshi Tabata, Yuan He, Yan Hu, Jiang Liu, A novel fundus imaging method based on a liquid lens focus scanning, 21st IEEE MDBS-BHE’ Symposium 2023 (HongKong, 2023.12.20) / (Oral)
40. Jiaqi Li, Lihui Wang*, Shaoyong Li, Lin Li, Lei Li, Active milliseconds zooming and tracking optics based on liquid lenses and a high-speed gaze controller, SPIE/COS Photonics Asia (Beijing, 2023.10.14) / (Oral 12765-4) doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2686749
41. Ronghua Hu, Hui Yang, Lihui Wang*, Longfei Fan, Research on a flexible optical tactile sensor based on a liquid lens structure, SPIE/COS Photonics Asia (Beijing, 2023.10.15) / (Oral 12771-12) doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2686776
42. Xiao Zhang, Lihui Wang*, Yuan He, Zhiwei Mou, Yiqi Cao, High-speed eye tracking based on a synchronized image acquisition mechanism by dual-ring infrared lighting source, SPIE/COS Photonics Asia (Beijing, 2023.10.15) / (Oral 12766-13) doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2686717
43. Huayu Cheng, Lihui Wang*, Yuan He, , High-speed all-in-focus 3D imaging technology based on the liquid lens focus scanning, SPIE/COS Photonics Asia (Beijing, 2023.10.16) / (Oral 12767-11) doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2686779
44. Shangen Tang, Lihui Wang*, Fengnian Song, Shaoyong Li, Dynamic projection mapping for non-planar objects with a variable focal lens, SPIE/COS Photonics Asia (Beijing, 2023.10.16) / (Oral 12767-12) doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2686766
45. Shuangjiang Huang, Lihui Wang*, Yuan He, Shi Bai, Measurement method of virtual image distance for near-eye display based on a variable-focus liquid lens, 12th Applied Optics and Photonics China (AOPC2023) (Beijing, 2023.07.25-26) / (Poster AOPC2023-09-022)
46. Huayu Cheng, Lihui Wang*, Yuan He, Yan Hu, Liu Jiang, High-speed all-in-focus 3D imaging method based on the liquid lens focus scanning, 12th Applied Optics and Photonics China (AOPC2023) (Beijing, 2023.07.25-26) / (Poster AOPC2023-09-020)
47. Xiao Zhang, Lihui Wang*, Yuan He, Zhiwei Mou, Yiqi Cao, High-speed eye tracking mechanism based on a synchronized image acquisition by dual-ring infrared lighting source, 12th Applied Optics and Photonics China (AOPC2023) (Beijing, 2023.07.25-26) / (Poster AOPC2023-09-021)
48. Shangen Tang, Lihui Wang*, Fengnian Song, Shaoyong Li, Dynamic projection mapping for non-planar objects with a variable focus lens, 12th Applied Optics and Photonics China (AOPC2023) (Beijing, 2023.07.25-26) / (Poster AOPC2023-06-007)
49. Jiaqi Li, Lihui Wang*, Lin Li, Shaoyong Li, Active milliseconds zooming and tracking optics based on liquid lenses and high-speed gaze control, 12th Applied Optics and Photonics China (AOPC2023) (Beijing,2023.07.25-26) / (Poster AOPC2023-09-023)
50. Jian Fu, Hui Yang, Ruimin Cao, Lihui Wang*, The Influence of Membrane Thickness on the Dynamic Response of Liquid Lens, Frontiers in Optics 2021 (FiO 2021)(Online Event. 2021.11.02)/ (Poster Session) JTu1A.131
51. Hui Yang, Jian Fu, Ruimin Cao, Lihui Wang*, An Optical Tactile Sensor with Liquid Lens Mechanism, Frontiers in Optics 2021 (FiO 2021)(Online Event. 2021.11.03)/ (Poster Session) JW7A.22
52. Ruimin Cao, Hui Yang, Jian Fu, Lihui Wang*, High-speed optical 3D active sensing method for high-dynamic targets in the large-field scene, Frontiers in Optics 2021 (FiO 2021)(Online Event. 2021.11.03)/ (Poster Session) JW7A.35
53. Lihui Wang, Satoshi Tabata, Hongjin Xu, Yunpu Hu, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, Interactive Dynamic Extended Depth-of-Field Projection Mapping with Variable Focus Lens and Visual Feedback Control, International Conference on Display Technology 2021, (Beijing, May 31, 2020)
54. Jian Fu, Ruimin Cao, Lihui Wang*, The influence of the apodization function on the optical needle, Frontiers in Optics 2020 (FiO 2020)(Online Event. 2020.09.14-17)/ (Poster Session)
55. Ruimin Cao, Lihui Wang*, Jian Fu, Adaptive self-window-based optical information acquisition method for high dynamic target, Frontiers in Optics 2020 (FiO 2020)(Online Event. 2020.09.16)/ (Oral Session)
56. Lihui Wang, Satoshi Tabata, Hirotoshi Takeuchi, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: A study for accelerating the speed of all-in-focus image processing, SPIE Photonics West 2020 (San Francisco, 2020.2.5)/Proceedings of SPIE Vol. 11245, Three-Dimensional and Multidimensional Microscopy: Image Acquisition and Processing XXVII; 112450U (2020) [DOI: 10.1117/12.2542686]
57. Hongjin Xu, Lihui Wang*, Satoshi Tabata, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: An extended depth-of-field projection method using a high-speed projector with a synchronized oscillating variable focus lens, SPIE Photonics West 2020 (San Francisco, 2020.2.5)/Proceedings of SPIE Vol.11304 , Advances in Display Technologies X, 113040T (2020) [DOI: 10.1117/12.2542477]
58. Lihui Wang, Yunpu Hu, Hongjin Xu, Masatoshi Ishikawa, A method for passive, monocular distance measurement of virtual image in VR/AR, The IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography 2019 (ICCP 2019) (Tokyo, Japan. 2019.05.15)/ [link]
59. Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Yunpu Hu, Satoshi Tabata, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic Depth-of-Field Projection for 3D Projection Mapping, ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI’19) (Glasgow, Scotland, UK. 2019.05.05-09) [DIO: 10.1145/3290607.3313246]
60. Lihui Wang, Yunpu Hu, Hongjin Xu, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic focal tracker display, SPIE Photonics West 2019 (San Francisco, California, USA. 2019.02.07)/ (Oral Session) [DIO: 10.1117/12.2506958]
61. Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Optical Mechanism controlled by Shape Memory Alloy Spring, 11th International Conference on Optics-Photonics Design and Fabrication (ODF’18, Hiroshima), (Hiroshima, Japan. 2018.11.29)/ (Poster Session) [Paper, 29PSb-36]
62. Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Solar Energy Actuated Optical Mechanism, OSA Light, Energy and the Environment Congress, (Singapore. 2018.11.06)/ (Poster Session) [DIO:10.1364/FTS.2018.JT2A.11]
63. Lihui Wang, Jianjiang Cui, Satoshi Tabata, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Readily Available Varifocal Microscope Imaging System, 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (Honolulu, Hawaii, USA. 2018.07.20)/ (Poster Session) [Paper, FrPoS-31.3]
64. Lihui Wang, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Investigation of the dynamic response performance for the liquid-filled variable focus lens, SPIE Photonics West 2018 (San Francisco, California, USA. 2018.01.31)/ (Poster Session) [DIO:10.1117/12.2288845]
65. Kenichi Murakami, Lihui Wang, Tomohiko Hayakawa, Taku Senoo, Masatoshi Ishikawa: Catching Robot Hand System in Dynamic Depth Variation with a Rotating Variable Focusing Unit, Frontiers in Optics 2017 (FiO 2017)(Washington DC, USA. 2017.9.19)/ (Poster Session) [DIO:10.1364/FIO.2017.JTu2A.52]
66. Lihui Wang, Tomohiko Hayakawa, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Depth of field extended imaging method based on intensification of time and spatial expansion, SPIE Smart Structures/NDE 2017(Portland, Oregon, USA. 2017.03.26)/ (Oral Session) [DIO:10.1117/12.2259891]
67. Lihui Wang, Tomohiko Hayakawa, Masatoshi Ishikawa, A fabrication method for variable focus micro lens array based on deformation of dielectric elastomer actuator, European Optical Society Bi-Annual Meeting (EOSAM) 2016 (Berlin, Germany. 2016.09.28)/ (Oral Session)
68. Tomohiko Hayakawa, Lihui Wang, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Three-dimensional scanning method based on deformation of a dielectric elastomer actuator, European Optical Society Bi-Annual Meeting (EOSAM) 2016 (Berlin, Germany. 2016.09.29)/ (Poster Session)
69. Tomohiko Hayakawa, Lihui Wang, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dielectric elastomer-based laser beam pointing method with ultraviolet and visible wavelength , SPIE Photonics West 2016 (San Francisco, California, USA. 2016.02.17)/ (Poster Session) [DOI:10.1117/12.2212081]
70. Tomohiko Hayakawa, Lihui Wang, Masatoshi Ishikawa, A Novel Precise Laser Manipulation Method with Dielectric Elastomer, OSA’s 99th annual meeting, Frontiers in Optics 2015 (FiO 2015)(San Jose, California, USA. 2015.10.19)/ (Oral Session) [DOI:10.1364/FIO.2015.FM2G.5]
71. Lihui Wang, Alvaro Cassinelli, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, A pair of diopter adjustable eyeglasses for presbyopia vision correction, SPIE Optics + Photonics 2014 (San Diego, California, USA, 2014.08.18) // Proc. of SPIE, Vol.9193, 91931G-1(Poster Session)[DOI:10.1117/12.2061659]
72. Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Adaptive achromatic doublet design by double variable-focus lenses, SPIE Optics + Photonics 2014 (San Diego, California, USA, 2014.08.17-21) / [(Oral Session)][DOI:10.1117/12.2061203]
73. Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, A Weak Power Enhanced Liquid-Membrane-Liquid Lens by a Pretension Elastic Membrane, OSA’s 97th annual meeting, Frontiers in Optics 2013/ Laser Science XXIX(FiO/LS 2013)(Orlando, Florida, USA, 2013.10.06-10)/ (Oral Session) [OSA Technical Digest FTu5F.5] [DOI: 10.1364/FIO.2013.FTu5F.5]
74. Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, A solution of pre-tension membrane for improving the usability of liquid-membrane-liquid lens in its weak power area, 2nd EOS Conference on Optofluidics 2013 (Munich, Germany, 2013.05.13-15) / (Oral Session)
75. Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Development of variable-focal lens with liquid-membrane-liquid structure and 30mm optical aperture, SPIE Photonics West 2013 (San Francisco, California, USA, 2013.02.02-07) / (Oral Session) [SPIE Proceedings 8617-5] [DOI:10.1117/12.2005531]
76. Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, A Liquid Lens with Liquid-Membrane-Liquid Structure, OSA’s 96th annual meeting, Frontiers in Optics 2012/ Laser Science XXVIII(FiO/LS 2012)(Rochester, NewYork, USA, 2012.10.14-18)/ (Oral Session)[OSA Technical Digest FM3A.3][DOI:10.1364/FIO.2012.FM3A.3]
77. Cui Jianjiang, Shi Dayu, Wang Lihui, Chen Dali, Liu Feng, Design and Realization of Route Control System in Railway System Based on Simulation, Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Logistics Systems and Intelligent Management (ICLSIM 2010), 2010: 989-993. [DOI: 10.1109/ICLSIM.2010.5461103(EI Index:11291780)]
78. Cui Jianjiang, Wang Lihui, Sun Lei, Zhang Yaowen, Wang Guoren, A Method of Near-Infrared Image Acquisition Based on Image Quality Assessment, Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Measurement and Control of Granular Materials (MCGM 2009), 2009: 509-512.
- Patents
1. プロジェクタの制御装置、プロジェクタ、投影システム、投影方法及びプログラム、渡辺義浩、王立輝、徐鴻金、東京大学、東京工業大学、PCT/JP2020/034180
(Projector and its control device, system, method, and program, Masatooshi Ishikawa, Yoshihiro Watanabe, Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, The University of Tokyo and Tokyo Institute of Technology, PCT/JP2020/034180)
2. 可変焦点レンズ、奥寛雅、王立輝、石川正俊、東京大学、PCT/JP2013/062988
(Variable focus lens, Hiromasa Oku, Lihui Wang, Masatoshi Ishikawa, The University of Tokyo, PCT/JP2013/062988)
3. (已授权)并联式运动目标视觉追踪装置
4. (已授权)三维空间激光投影切片显示装置
5. (已授权)按压式触觉传感器
6. (已授权)叶片追光及摄像装置
7. (已授权)阵列式触觉传感器
8. (已授权)一种光学传感装置、传感设备及系统
9. (审查中)(PCT)一种反射式高速自动追光设备
10. (审查中)动态监控摄像装置和动态监控方法
11. (审查中)视觉防抖装置和方法
12. (审查中)液体透镜运行调控系统、液体透镜运行调控方法及装置
Media and others
1. Dynamic Projection Mapping
1) ITmedia News. 液体レンズを用いた高速焦点追従投影システム[https://dip-labs.com/news/20210128-01/] (2021.01) (日本語)
译:ITmedia News,基于液体的动态光雕投影系统。
2) 中国科技网/科技日报. “液体透镜带来光学镜头革命” [http://www.stdaily.com/index/kejixinwen/2019-11/21/content_817911.shtml?from=singlemessage](2019.11) (in Chinese)
3) 日刊工業新聞. “動く物体に絵を投影できるプロジェクション技術、どんな用途に使う”[https://newswitch.jp/p/20672?fbclid=IwAR3MP-srPICwf7SsFN333tQQ-9pA-Jddmu1eq8ElD61jKqIMw6nge9yeGrU] (2020.01) (in Japanese)
译:日刊工业新闻。可在移动物体表面绘画的光雕投影技术,潜在用途是?
2. Variable Focus Lens
1) テレビ東京ワールドビジネスサテライトトレンドたまご[オートフォーカスの老眼鏡!?] [https://txbiz.tv-tokyo.co.jp/wbs/trend_tamago/post_124134/] (2017.01) (in Japanese)
译:东京电视台,全球财经卫视Trend Tamago专题,自动对焦老花眼眼镜!
3. 3D AR Head-Up-Display for ADAS Automotive
1) Konica Minolta Release. “Konica Minolta Develops the World’s First* Automotive 3D Augmented Reality Head-up Display” [https://www.konicaminolta.com/newsroom/2017/0227_01_01.html]. (2017.02)
2) コニカミノルタニュースリリース.“コニカミノルタ 世界初*の車載用3D 拡張現実ヘッドアップディスプレイを開発” [https://www.konicaminolta.com/jp-ja/newsroom/2017/0113_01_01.html]. (2017.01) (in Japanese)
3) 日本経済新聞. “車載用3D拡張現実ヘッドアップディスプレーを開発” [https://www.nikkei.com/article/DGXLRSP433224_T10C17A1000000/].(2017.01) (in Japanese)
欢迎感兴趣的研究者和同学联系。
wanglihui[at]suda.edu.cn
王立辉,男,辽宁辽阳人,苏州大学教授,博导,日本东京大学博士,正高级工程师。中国民主建国会会员,地方政协委员,广州欧美同学会番禺分会副会长,广东省康复医学发展研究会理事,民建广州科信委副主任、民建广东科信委委员。历任日本东京大学特聘研究员、特聘助理教授,广东省科学院半导体研究所智能光电方向学科带头人。获广东省“珠江人才计划”引进高层次人才(青年拔尖),广东省科学院“百人计划”引进高层次人才、杰出青年、优秀青年等。电气与电子工程师学会IEEE、国际光学工程学会SPIE、美国光学学会Optica等高级会员Senior Member。
在日本东京大学留学任教期间的十余年间,师从东京大学原副校长、产学研部长、日本工程院院士石川正俊(Masatoshi Ishikawa)教授,在研究组内进行以高速视觉为核心的技术攻关,长期从事新一代超高速机器视觉和动态三维显示系统的技术研发工作。通过观察发现在毫秒级高速机器视觉系统中,传统的光学系统已经成为整个系统的瓶颈,提出利用透明液体来替代传统固体镜头,成功研发世界首台大口径全焦点高分辨率可变焦液体镜头,并将其推广至高速机器视觉及可穿戴智能眼镜等领域,其间课题曾获日本文部科学省博士生奖学金、青年基金、卓越研究员候选人,此外该成果受到日本东京电视台全球财经卫视Trend Tamago专题报道,并作为中国科技部部长和重大专项办公室主任访问东京大学时接待参观项目之一,受到了学术界及商业的密切关注。协同柯尼卡美能达公司合作研发的世界首台用于汽车辅助(自动)驾驶系统(ADAS)的三维增强现实抬头显示器,分别出展日本东京全球汽车技术博览会和德国汉诺威工业展会,备受汽车界高度关注。近年成功研发出为医学领域中的治疗计划系统的动态三维显示器,为医疗三维图像提供动态三维低延迟的人机交互环境。成果出展于世界顶级人机交互学年会(ACM CHI)、美国计算机图形学年会(ACM SIGGRAPH )和日本数字信息展会出展,并荣获美国计算机图形学会特别奖(ACM SIGGRAPH Special Prize)、日本经济产业省数字信息协会科技创新奖(Innovative Technologies )和赞助商奖(CG World Sponsor Award)、IRCE2025国际会议最佳组织奖、华创杯及深创赛等赛事奖励。以第一或通讯作者在Soft Robotics、Nano Energy、IEEE、Optics Express、Applied Optics等发表科研论文80余篇,申请授权国内外发明专利十余件,并多次受到日本东京电视台、日刊产业新闻、日本经济新闻、中国科技日报等国内外媒体报道。
研究方向凝练并融合了光、机、电、信息工程领域的科学知识。具体成果可广泛应用于,高速机器视觉,商业广播设备,高速自动对焦,全焦点摄影,高速图像追踪,三维重建,生物医疗,安防监控,动态光雕投影,虚拟/增强/混合现实技术,汽车辅助驾驶,自动驾驶等领域。
____
参考链接:
1. Dynamic Image Perception Labs: https://diplabs.wordpress.com/
2. Researchgate: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Lihui-Wang-7
3. ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3261-3728
4. Mentors: Prof. Dr. Masatoshi Ishikawa (Link, Lab Link), Prof. Dr. Hiromasa Oku (Link, Lab Link)
王立辉,辽宁辽阳人,苏州大学教授,博导,日本东京大学博士,正高级工程师,省级人才,民建会员,地方政协委员。
About/关于
人类社会的周围环境具有高速变化的动态特性,若对此变化的环境对象进行实时观测与交互,传统的采集方法和检测手段将面临很大的瓶颈。
动态图像感知(Dynamic Image Perception)名字的由来,源自日本東京大学石川正俊教授(Masatoshi Ishikawa)研究室,时任组长奥宽雅博士(Hiromasa Oku)发起的Dynamic Image Control课题组名,研究室倡导通过光、机、电、信息一体化的全局调控方式,在时间维度和空间维度上超越人类视觉感知。
Object/着眼点
研究方向围绕超高速视觉展开,以高速对焦和高速追踪为着眼点,解决以高速移动物体为采集对象时的“看不见”和“看不清”的“卡脖子”难题, 并在此基础上进一步拓展高速高清机器视觉和高速动态显示交互技术。
Originality/独创性
凝练并融合了光、机、电、信息工程领域的科学知识,以周边高速变化的动态信息为观测对象,发展新一代视觉信息感知、分析处理和显示技术。
Research and Applications/研究范围及应用场景
- 光学仪器、自适应光学设备(变焦/调焦液体透镜、智能老花眼眼镜;超高速视觉追踪)
- 先进制造、智能制造(高器视觉、机器人导航控制;柔性传感器、精密器件抓取)
- 安防、监控摄像设备(高速目标追踪、可疑目标提示)
- 新型显示、虚拟/增强/混合现实(动态光雕投影显示技术;三维车载抬头显示器;医疗手术辅助导航)

In Detail/具体展开
1 Active Vision/主动视觉
1-1 Variable Focus Lens/可变焦液体透镜
In order to change focus with traditional solid lenses, which have fixed optical properties, two or more lenses have to be jointly moved mechanically. In contrast, a variable focus lens can dynamically control its focal length by only using a single lens element. Liquid-filled variable focus lenses are based on the physical deformation of refractive surfaces, which changes their curvature.
We proposed a novel variable focus lens with a large optical aperture. The lens consists of two chambers separated by a membrane. The chambers were infused with two different liquids characterized by their similar density but different refractive indices. Thus its deformation was in the interface between the two liquids, and it acted as a refractive surface due to the difference in refractive index of these liquids. If one fluid was made to flow into and out of its chamber, while the other was locked, the lens could shift its power dynamically by means of a syringe pump.
|
|
自研可变焦距液体透镜(大口径版) A photograph of the lens prototype. | 可变焦距液体透镜的性能测试展示 Experimental view of its variable focus performance. |
|
|
可便携式可变焦距液体透镜 Waearable liquid-based tunable lens | 可便携式液体透镜(东京电视台专题报道) Waearable liquid-based tunable lens |
Reference/ 参考
Zenghong Duan, Lihui Wang*, Zhi Li, Jian Fu, Susheng Fu, Boqian Chen, Yuxun Chen, and Yong Zhao, “Dynamic performance of a membrane-based variable focus lens with a large aperture,” Appl. Opt. 62, 4609-4617 (2023)[DOI:10.1364/AO.486278]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Paraxial ray solution for liquid-filled variable focus lenses, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Volume 56, Number 12, 122501 (2017)[DOI:10.7567/JJAP.56.122501]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, An improved low-optical-power variable focus lens with a large aperture, Optics Express, Vol.22, Issue 16, pp. 19448-19456 (2014)[DOI:10.1364/OE.22.019448]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Variable-focus lens with 30 mm optical aperture based on liquid-membranes-liquid structure, Applied Physics Letters, Vol.102, 131111 (2013)[DOI:10.1063/1.4800603]
1-2 High-speed Active Visual Tracking/高速主动视觉追踪
在追踪具有高度非线性的高速随机运动目标时,传统光电主动视觉系统存在目标丢失、视觉追踪失效的问题。课题组通过搭建一套毫秒级光电主动视觉系统。采用光电云台结构、感兴趣区域提取、并行计算、高速运动目标追踪算法,实现毫秒级目标跟踪。
|
|
| 高速视觉追踪效果图. (a)目标从右至左运动过程; (b) 目标下落-碰撞地面-弹起的高动态过程。 | 球类高速运动的实时追踪,高速主动视觉系统,可以时刻保持观测对象在计算机视野中心(ball real-time tracking) |
|
|
| 6自由度实时追踪测试( test for 6-dof tracking) | 乒乓球拍6自由度实时追踪(tracking pingpang pat 6-DOF) |
Reference/参考
Jiaqi Li, Lin Li, Lihui Wang*, Lei LI, Shaoyong Li, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, Adaptive milliseconds tracking and zooming optics based on a high-speed gaze controller and liquid lenses, Optics Express, Vol.32, Issue 2, pp. 2257-2270 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/OE.512003]
Ruimin Cao, Jian Fu, Hui Yang, Lihui Wang*, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, “Robust optical axis control of monocular active gazing based on pan-tilt mirrors for high dynamic targets,” Optics Express 29, 40214-40230 (2021) [DOI: 10.1364/OE.439083]
3 High-Speed 3D & Depth Imaging/成像
A large open aperture in an optical system can capture high-resolution images but yields a shallow depth of field. In order to keep the high-resolution and enlarge the DOF at the same time, back-and-forth movement of the lens should be driven by the rack and pinion motion of a motor. However, continual forward and reverse rotation is a high-power-consumption task, because positive and negative current are used alternately to control the motor, which quickly triggers a safety stop to prevent overheating. Moreover, it is quite difficult to achieve high-speed responses in such conditions.
|
|
| 倾斜放置的芯片(传统成像方式导致局部信息清晰,局部星系模糊的典型案例) | 高速焦点扫描成像方式,短时间内采集12张不同景深图像(左下),通过自研图像处理算法,实时生成全焦点图(右上) |
|
|
| 眼底模型(大景深物体) | 实时对焦点扩展景深成像(shape from focus) |
Reference/参考
Huayu Cheng, Lihui Wang*, Satoshi Tabata, Yuan He, Yan Hu, Jiang Liu and Zhiwei Mou, High-speed all-in-focus 3D imaging method based on the liquid lens focus scanning, Applied Optics, Vol.63, Issue 21, pp. 5602-5610 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/AO.523864]
Lihui Wang, Jianjiang Cui, Satoshi Tabata, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Low-cost, readily available 3D microscopy imaging system with variable focus spinner, Optics Express, Vol.26, Issue 23, pp. 30576-30587 (2018).[DOI:10.1364/OE.26.030576]
4 High-Speed 3D Projection Mapping/显示
Projection mapping (PM) is attractive as a fundamental technology for the advancement of various subjects, such as media art, entertainment, and augmented reality. However, conventional projectors have a shallow depth of field (DOF); therefore, sharp images are only visible in the limited depth range. In the case of dynamic projection mapping (DPM), which can project images on the surface of the moving objects, the shallow DOF limits the permissible motion of the object, because the projected images become blurred when the object is outside the DOF.
Our laboratories have developed a high-speed focal tracking projection system, which includes the technologies of high-speed vision, high-speed projector, and high-speed variable focus optics. In this system, the variation of the object’s distance and posture was captured using the high-speed vision technology that served as immediate feedback to the liquid lens and high-speed projector. As a result, the focal distance is compensated, and the projected images are updated in real-time to fit the moving object. Therefore, a well-focused image projection was achieved even when the motion involved large depth range movement.
This system could ensure that the projected images were sharp and clear at variable distances, while the object was moving dynamically in a large three-dimensional area. Hence, this approach can be effectively applied to applications such as Volume Slicing Display. Furthermore, it can turn any physical surface into an interactive display, and enable the manipulation of their appearance to provide detailed information. Our system provides the essential technology for expanding such applications.
|
|
| Prototype of projection tracking system using a liquid lens. (Ver.7) (2018-) | Prototype of projection tracking system using a liquid lens. (Ver.2) (2019-) |
|
| Volume Slicing Display: change images based on the distance. |
|
|
|
提案系统能实时保持投影对焦清晰(左侧图为本系统)our projector is always in focus (left) | 即使投影对象时刻旋转,投影信息能根据旋转反馈调整/Target rotationcan be detected self adjust projection | 医疗用三维数据信息能够在三维空间内做高清切片投影展示/ 3D CT data can be projected and shown with slicing display |
本技术与2019年11月19日获得日本经济产业省数字信息科技创新奖、美国计算机图形学会特等奖、日本CGWorld赞助商奖三项奖励。此次授奖也是日本数字信息展,首次将三个奖项同时授予同一项技术。
The following three awards were given to the project “High-speed focal tracking projection system based on liquid lens”.
ACM SIGGRAPH Special Prize, (Association for Computing Machinery)
Innovative Technologies 2019, (Digital Content Association of Japan)
Innovative Technologies 2019, Sponsor Award (CGWORLD) 2019, (Digital Content Association of Japan)
Reference/ 参考
Lihui Wang*, Satoshi Tabata, Hongjin Xu, Yunpu Hu, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic depth-of-field projection mapping method based on a variable focus lens and visual feedback, Optics Express, 31(3), pp. 3945-3953 (2023) [DOI:10.1364/OE.478416]
Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Satoshi Tabata, Yunpu Hu, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: High-Speed Focal Tracking Projection Based on Liquid Lens, ACM SIGGRAPH 2020 Emerging Technologies (SIGGRAPH ’20) (Virtual Event, USA, 2020.8.24-28) [DOI: 10.1145/3388534.3408333]
Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Yunpu Hu, Satoshi Tabata, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic Depth-of-Field Projection for 3D Projection Mapping, ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI’19) (Glasgow, Scotland, UK. 2019.05.05-09) [DOI: 10.1145/3290607.3313246]
5 3D Augmented Reality Head-Up-Display / 三维增强现实车载抬头显示器
Head-Up-Display (HUD) enables a driver to view information with his head positioned “up” and looking forward, instead of angled down looking at lower instruments. By adding the Augmented Reality technology, targets, like people and cars, can be marked to alarm to the drivers to avoid the potential accidents.
Traditional 2D AR HUD projects information messages at a certain distance away from the driver. It asks a driver to observe the projection along the optical axis at a certain point. When the driver moves his head, a miss-matching projection occurs between the projected data and the target in the real world.
In this 3D AR HUD technology, a 3D virtual display can be projected in front of the driver. AR messages will be dynamically projected according to the 3D locations of the targets. In our 3D HUD, a virtual display is projected into a three-dimensional world, so there will be no mismatch when the driver moves.
The following demos were recorded by two cameras, which were placed at different places. When the camera was placed along the optical axis, 2D and 3D markers were all perfectly matched. When the camera was placed at an angle to the optical axis, a mismatch was found in 2D HUD, but 3D HUD was still well matched.
This work was conducted by a collaborate research project with Ishikawa Laboratory and Konica Minolta Inc..
|
|
|
| A photo of 2D HUD projection. All the 2D HUD markers were projected at a certain distance. | A photo of 3D HUD projection. 3D HUD markers were projected at different distance. This photo were token when it focused at close. | A photo of 3D HUD projection. 3D HUD markers were projected at different distance. This photo were token when it focused at far. |
6 Smart Actuator and sensor/软体驱动器和传感器
力触觉感知和交互作为人-机交互的主要方式之一,其通常需要人工设备具备良好的柔性触觉感知能力。为丰富人工设备所能感知的触觉信息,基于混合感知机理的触觉传感器近年来受到了广泛关注。然而,对于可穿戴或柔性人工设备而言,开发具有简单结构、易制备、成本低、功耗低、易于维护和集成的触觉传感器仍然是一项艰巨挑战。
|
|
| 自研基于液体透镜的柔性触觉感知器,抓取柔性物体 | 基于力反馈控制实现对超软物体的无损抓取 |
Reference/参考
Hui Yang, Tianzhao Bu*, Wenbo Liu, Jiaqi Liu, Yunzhi Ling, Meixia Wu, Weirui Liu, Changan Wang*, Xifeng Gao*, Lihui Wang*, A novel triboelectric-optical hybrid tactile sensor for human-machine tactile interaction, Nano Energy, 125, pp. 109592 (2024) [DOI:10.1016/j.nanoen.2024.109592] (IF=17.6)
Ronghua Hu, Hui Yang, Lihui Wang*, and Longfei Fan, Flexible optical tactile sensor based on a liquid-membrane lens structure, Applied Optics, 62(26), 6952-6960 (2023) [DOI:10.1364/AO.496741](IF=1.905)
Hui Yang, Jiaqi Liu, Wenbo Liu, Weirui Liu, Zilong Deng, Yunzhi Ling, Changan Wang, Meixia Wu, Lihui Wang*, and Li Wen*, Compliant Grasping Control for a Tactile Self-Sensing Soft Gripper, Soft Robotics, (2023) [DOI:10.1089/soro.2022.0221] (IF=7.784)
Media and others (媒体报道等)
1. Dynamic Projection Mapping(动态光雕投影)
1) ITmedia News. 液体レンズを用いた高速焦点追従投影システム[https://dip-labs.com/news/20210128-01/] (2021.01) (日本語)
译:ITmedia News,基于液体的动态光雕投影系统。
2) 中国科技网/科技日报. “液体透镜带来光学镜头革命” [http://www.stdaily.com/index/kejixinwen/2019-11/21/content_817911.shtml?from=singlemessage](2019.11) (in Chinese)
3) 日刊工業新聞. “動く物体に絵を投影できるプロジェクション技術、どんな用途に使う”[https://newswitch.jp/p/20672?fbclid=IwAR3MP-srPICwf7SsFN333tQQ-9pA-Jddmu1eq8ElD61jKqIMw6nge9yeGrU] (2020.01) (in Japanese)
译:日刊工业新闻。可在移动物体表面绘画的光雕投影技术,潜在用途是?
2. Variable Focus Lens(可变焦液体镜头)
1) テレビ東京ワールドビジネスサテライトトレンドたまご [オートフォーカスの老眼鏡!?] [https://txbiz.tv-tokyo.co.jp/wbs/trend_tamago/post_124134/] (2017.01) (in Japanese)
译:东京电视台,全球财经卫视Trend Tamago专题,自动对焦老花眼眼镜!
3. 3D AR Head-Up-Display for ADAS Automotive(车载三维抬头显示器)
1) Konica Minolta Release. “Konica Minolta Develops the World’s First* Automotive 3D Augmented Reality Head-up Display” [https://www.konicaminolta.com/newsroom/2017/0227_01_01.html]. (2017.02)
译:柯尼卡美能达,世界首发车载三维增强现实抬头显示器
2) コニカミノルタニュースリリース.“コニカミノルタ 世界初*の車載用3D 拡張現実ヘッドアップディスプレイを開発” [https://www.konicaminolta.com/jp-ja/newsroom/2017/0113_01_01.html]. (2017.01) (in Japanese)
译:柯尼卡美能达,世界首发车载三维增强现实抬头显示器
3) 日本経済新聞. “車載用3D拡張現実ヘッドアップディスプレーを開発” [https://www.nikkei.com/article/DGXLRSP433224_T10C17A1000000/].(2017.01) (in Japanese)
译:日本经济新闻,车载三维增强现实抬头显示器
更加详细的研究信息可参考:diplabs.wordpress.com
欢迎对光机电一体化、液态透镜、高速视觉追踪、动态投影/AR/VR交互等方向感兴趣的老师同学联系!
长期同東京大学、東京理科大学、東京科学大学、群馬大学、香港理工大学、香港城市大学等高校合作!
欢迎以下专业代码的同学联系,名额充足,谢谢关注(^_^)v.
》请发电邮到wanglihui@suda.edu.cn,标题(x级-x大学-x专业--姓名),并附个人简历,谢谢。
》为保证公平录取,准备推免和考研复试中的同学们,待明确录取资格后再联系,祝你们好运!
081200 计算机科学与技术(学硕)
085410 人工智能(专硕)
080200 机械工程(学硕)
085501 机械工程(专硕)
Team/团队
| 副教授/Assoc. Prof. | 胡衍/Yan Hu(兼) |
| 讲师/Lecture | 李璐/Lu Li |
| 工程师/Engineer | 彭翠玲 博士/Dr. Cuiling Peng(兼); 胡书赫/Shuhe Hu(兼) |
| 博士生/Ph.d Student | 黄双江/Shuangjiang Huang(高速视觉及姿态检测) 段增鸿/Zenghong Duan(可变焦镜头及运动控制) 孙浩楠/Haonan Sun(高速机器视觉感知) |
| 硕士生/M.S. Student | 桂旭/Xu Gui(高速视觉追踪及位姿检测) |
王迦羽/Jiayu Wang(高速视觉及人机交互) 彭贵远/Guiyuan Peng(高速视觉追踪) 沈寅驰/Yinchi Shen(可变焦镜头开发) 张超洋/Chaoyang Zhang(高速视觉检测) | |
高莉婷/Liting Gao 蔡华宏/Huahong Cai 孙浩/Hao Sun 李文致/Wenzhi Li 何瑞昭/Ruizhao He | |
| 本科生/Bachelor Student | ... ... |
| 访问生/Visit Student | 张峻豪/Junhao Zhang |
教师室:未来科创中心513
学生室:未来科创中心611
实验室:未来科创中心705-1-2、1201-1-5
Alumni/毕业生
| 科研骨干/Staff | ||
| 2020.12-2024.03 | 杨辉/Hui Yang | 高校教师 |
| 2020.05-2021.12 | 付健/Jian Fu | 高校教师 |
| 2019.10-2021.12 | 曹瑞珉/Ruimin Cao | 高企就职 |
| 学生/ Student | ||
| 研究生/Master | ||
| 2023.09-2025.06 | 黄宇韬/Yutao Huang | 海外留学读博(*校优秀毕业论文) |
| 陈显华/Xianhua Chen | 上市公司就职 | |
| 许凯涵/Kaihan Xu | 高校教师 | |
| 2022.09-2024.06 | 张潇/Xiao Zhang | 海外留学读博 |
| 程铧钰/Huayu Cheng | 高校教师 | |
| 黎嘉祺/Jiaqi Li | 海外留学读博 | |
| 唐山根/Shangen Tang | 高校教师 | |
| 胡荣桦/Ronghua Hu | 高企就职 | |
| 2021.09-2023.06 | 宋丰年/Fengnian Song | 高企就职 |
| 本科生/Bachelor | ||
| 2024.12-2025.06 | 周锦枝/Jinzhi Zhou | 攻读硕士 |
| 郑胜楠/Shengnan Zheng | 攻读硕士 | |
| 罗仕权/Shiquan Luo | 企业就职 | |
| 实习生/Intern | ||
| 2022.07-2022.08 | 钦壮飞/Zhuangfei Qin | 海外留学 |
| 2021.08-2021.12 | 李嘉驹/Jiaju Li | 企业就职 |
| 林文裕/Wenyu Lin | 企业就职 | |
| 本科生成长陪伴 | ||
| 2024.09-2025.06 | 黄广维(导生,22级机械电子) | |
| 团队43 | 胡泽嘉、吴胤霖、潘浩宇、何玖 鹏(学生,24级机械电子) |
Album/相册
2025-09-20 |
|
2024-12-11 |
2024-09-23 |
2024-04-10 |
1 Active Vision/主动视觉
1-1 Variable Focus Lens/可变焦液体透镜
In order to change focus with traditional solid lenses, which have fixed optical properties, two or more lenses have to be jointly moved mechanically. In contrast, a variable focus lens can dynamically control its focal length by only using a single lens element. Liquid-filled variable focus lenses are based on the physical deformation of refractive surfaces, which changes their curvature.
We proposed a novel variable focus lens with a large optical aperture. The lens consists of two chambers separated by a membrane. The chambers were infused with two different liquids characterized by their similar density but different refractive indices. Thus its deformation was in the interface between the two liquids, and it acted as a refractive surface due to the difference in refractive index of these liquids. If one fluid was made to flow into and out of its chamber, while the other was locked, the lens could shift its power dynamically by means of a syringe pump.
|
|
A cross-sectional view of the lens system. | A photograph of the lens prototype. |
Reference/ 参考
Zenghong Duan, Lihui Wang*, Zhi Li, Jian Fu, Susheng Fu, Boqian Chen, Yuxun Chen, and Yong Zhao, “Dynamic performance of a membrane-based variable focus lens with a large aperture,” Appl. Opt. 62, 4609-4617 (2023)[DOI:10.1364/AO.486278]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Paraxial ray solution for liquid-filled variable focus lenses, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Volume 56, Number 12, 122501 (2017)[DOI:10.7567/JJAP.56.122501]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, An improved low-optical-power variable focus lens with a large aperture, Optics Express, Vol.22, Issue 16, pp. 19448-19456 (2014)[DOI:10.1364/OE.22.019448]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Variable-focus lens with 30 mm optical aperture based on liquid-membranes-liquid structure, Applied Physics Letters, Vol.102, 131111 (2013)[DOI:10.1063/1.4800603]
1-2 Active Visual Tracking/主动视觉追踪
在追踪具有高度非线性轨迹的高速随机运动目标时,传统光电主动视觉系统存在目标丢失、视觉追踪失效的问题。课题组通过搭建了一套毫秒级光电主动视觉系统。采用光电云台结构、感兴趣区域提取、并行计算、高速运动目标追踪算法,实现响应时间≤2ms毫秒级的目标跟踪。
|
|
| 高速视觉追踪效果图. (a)目标从右至左运动过程; (b) 目标下落-碰撞地面-弹起的高动态过程。 | 视频. 基于毫秒级光电主动视觉系统的高动态目标追踪实验 |
Reference/参考
Jiaqi Li, Lin Li, Lihui Wang*, Lei LI, Shaoyong Li, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, Adaptive milliseconds tracking and zooming optics based on a high-speed gaze controller and liquid lenses, Optics Express, Vol.32, Issue 2, pp. 2257-2270 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/OE.512003]
Ruimin Cao, Jian Fu, Hui Yang, Lihui Wang*, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, “Robust optical axis control of monocular active gazing based on pan-tilt mirrors for high dynamic targets,” Optics Express 29, 40214-40230 (2021) [DOI: 10.1364/OE.439083]
3 High-Speed 3D & Depth Imaging/成像
A large open aperture in an optical system can capture high-resolution images but yields a shallow depth of field. In order to keep the high-resolution and enlarge the DOF at the same time, back-and-forth movement of the lens should be driven by the rack and pinion motion of a motor.
However, continual forward and reverse rotation is a high-power-consumption task, because positive and negative current are used alternately to control the motor, which quickly triggers a safety stop to prevent overheating. Moreover, it is quite difficult to achieve high-speed responses in such conditions.
|
Images obtained by changing the plate thickness from 0 mm to 11 mm. (a) Raw image sequence. (b) Images obtained after rescaling, phase correction, and Laplacian edge detection. (c) All-in-focus sharp image generated by merging the in-focus pixels. (d) Depth map produced by using the index numbers of the images, which contained depth information. |
Reference/参考
Huayu Cheng, Lihui Wang*, Yuan He, , High-speed all-in-focus 3D imaging technology based on the liquid lens focus scanning, SPIE/COS Photonics Asia (Beijing, 2023.10.16) / (Oral 12767-11) doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2686779
Lihui Wang, Jianjiang Cui, Satoshi Tabata, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Low-cost, readily available 3D microscopy imaging system with variable focus spinner, Optics Express, Vol.26, Issue 23, pp. 30576-30587 (2018).[DOI:10.1364/OE.26.030576]
4 High-Speed 3D Projection Mapping/显示
Projection mapping (PM) is attractive as a fundamental technology for the advancement of various subjects, such as media art, entertainment, and augmented reality. However, conventional projectors have a shallow depth of field (DOF); therefore, sharp images are only visible in the limited depth range. In the case of dynamic projection mapping (DPM), which can project images on the surface of the moving objects, the shallow DOF limits the permissible motion of the object, because the projected images become blurred when the object is outside the DOF.
Our laboratories have developed a high-speed focal tracking projection system, which includes the technologies of high-speed vision, high-speed projector, and high-speed variable focus optics. In this system, the variation of the object’s distance and posture was captured using the high-speed vision technology that served as immediate feedback to the liquid lens and high-speed projector. As a result, the focal distance is compensated, and the projected images are updated in real-time to fit the moving object. Therefore, a well-focused image projection was achieved even when the motion involved large depth range movement.
This system could ensure that the projected images were sharp and clear at variable distances, while the object was moving dynamically in a large three-dimensional area. Hence, this approach can be effectively applied to applications such as Volume Slicing Display. Furthermore, it can turn any physical surface into an interactive display, and enable the manipulation of their appearance to provide detailed information. Our system provides the essential technology for expanding such applications.
|
|
| Prototype of projection tracking system using a liquid lens. (Ver.7) (2018-) | Prototype of projection tracking system using a liquid lens. (Ver.2) (2019-) |
|
| System configuration. |
|
| In-focus projection in the large depth range. |
|
| Volume Slicing Display: change images based on the distance. |
The following three awards were given to the project “High-speed focal tracking projection system based on liquid lens”.
ACM SIGGRAPH Special Prize, (Association for Computing Machinery)
Innovative Technologies 2019, (Digital Content Association of Japan)
Innovative Technologies 2019, Sponsor Award (CGWORLD) 2019, (Digital Content Association of Japan)
Reference/ 参考
Lihui Wang*, Satoshi Tabata, Hongjin Xu, Yunpu Hu, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic depth-of-field projection mapping method based on a variable focus lens and visual feedback, Optics Express, 31(3), pp. 3945-3953 (2023) [DOI:10.1364/OE.478416]
Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Satoshi Tabata, Yunpu Hu, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: High-Speed Focal Tracking Projection Based on Liquid Lens, ACM SIGGRAPH 2020 Emerging Technologies (SIGGRAPH ’20) (Virtual Event, USA, 2020.8.24-28) [DOI: 10.1145/3388534.3408333]
Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Yunpu Hu, Satoshi Tabata, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic Depth-of-Field Projection for 3D Projection Mapping, ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI’19) (Glasgow, Scotland, UK. 2019.05.05-09) [DOI: 10.1145/3290607.3313246]
Lihui Wang, Yunpu Hu, Hongjin Xu, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic focal tracker display, SPIE Photonics West 2019 (San Francisco, California, USA. 2019.02.07)/ (Oral Session) [DOI: 10.1117/12.2506958]
5 3D Augmented Reality Head-Up-Display / 三维增强现实车载抬头显示器
Head-Up-Display (HUD) enables a driver to view information with his head positioned “up” and looking forward, instead of angled down looking at lower instruments. By adding the Augmented Reality technology, targets, like people and cars, can be marked to alarm to the drivers to avoid the potential accidents.
Traditional 2D AR HUD projects information messages at a certain distance away from the driver. It asks a driver to observe the projection along the optical axis at a certain point. When the driver moves his head, a miss-matching projection occurs between the projected data and the target in the real world.
In this 3D AR HUD technology, a 3D virtual display can be projected in front of the driver. AR messages will be dynamically projected according to the 3D locations of the targets. In our 3D HUD, a virtual display is projected into a three-dimensional world, so there will be no mismatch when the driver moves.
The following demos were recorded by two cameras, which were placed at different places. When the camera was placed along the optical axis, 2D and 3D markers were all perfectly matched. When the camera was placed at an angle to the optical axis, a mismatch was found in 2D HUD, but 3D HUD was still well matched.
This work was conducted by a collaborate research project with Ishikawa Laboratory and Konica Minolta Inc..
|
|
|
| A photo of 2D HUD projection. All the 2D HUD markers were projected at a certain distance. | A photo of 3D HUD projection. 3D HUD markers were projected at different distance. This photo were token when it focused at close. | A photo of 3D HUD projection. 3D HUD markers were projected at different distance. This photo were token when it focused at far. |
6 Smart Actuator and sensor/软体驱动器和传感器
触觉感知和交互作为人-机交互的主要方式之一,其通常需要人工设备具备良好的触觉感知能力。为丰富人工设备所能感知的触觉信息,基于混合感知机理的触觉传感器近年来受到了广泛关注。然而,对于可穿戴或柔性人工设备而言,开发具有简单结构、易制备、成本低、功耗低、易于维护和集成的触觉传感器仍然是一项艰巨挑战。
在此背景下研究团队提出了一种新型的摩擦电-光电混合触觉传感器,其采用模块化分体式结构,包括两个单元:基于单电极摩擦电纳米发电机设计的摩擦电单元,用于接收外部触觉刺激;以及基于可变焦液体透镜结构的光电单元,用于将触觉刺激转化为光电信号。两个单元均采用单腔体结构,可轻松实现对单元零部件的拆卸与更换。此外,摩擦电单元可根据其输出信号控制光电单元内部所嵌光源的开/关行为,从而降低传感单元功耗,提高触觉响应速度。光电单元具有优越的电磁干扰抗性,使得传感器能够准确、定量地感知接触力。通过开展感知性能测试实验,表现出响应时间短(~9 ms)、输出线性度高(R2≈0.9952)、耐久性和稳定性好等特点。基于上述特点,通过进一步设计-开展文字键入、图形绘制、音乐演奏等触觉交互实验,展示了本传感器在触觉交互任务中的实用性,进而说明其在人-机交互设备领域中具有广阔的应用前景。
|
| 如图,(左上)摩擦电-光电混合触觉传感器结构图,(右上)传感器得动作机理,(左下、右下)面向摩斯电码、迷宫游戏和绘图操作功能,传感器按钮的人机交互配置方案。 |
Reference/参考
Hui Yang, Tianzhao Bu*, Wenbo Liu, Jiaqi Liu, Yunzhi Ling, Meixia Wu, Weirui Liu, Changan Wang*, Xifeng Gao*, Lihui Wang*, A novel triboelectric-optical hybrid tactile sensor for human-machine tactile interaction, Nano Energy, 125, pp. 109592 (2024) [DOI:10.1016/j.nanoen.2024.109592] (IF=17.6)
Ronghua Hu, Hui Yang, Lihui Wang*, and Longfei Fan, Flexible optical tactile sensor based on a liquid-membrane lens structure, Applied Optics, 62(26), 6952-6960 (2023) [DOI:10.1364/AO.496741](IF=1.905)
Hui Yang, Jiaqi Liu, Wenbo Liu, Weirui Liu, Zilong Deng, Yunzhi Ling, Changan Wang, Meixia Wu, Lihui Wang*, and Li Wen*, Compliant Grasping Control for a Tactile Self-Sensing Soft Gripper, Soft Robotics, (2023) [DOI:10.1089/soro.2022.0221] (IF=7.784)
| 博士生/Ph.d Student | 黄双江/Shuangjiang Huang |
| 硕士生/M.S. Student | 张潇/Xiao Zhang;程铧钰/Huayu Cheng 黎嘉祺/Jiaqi Li;唐山根/Shangen Tang;胡荣桦/Ronghua Hu |
| 许凯涵/ Kaihan Xu;陈显华/Xianhua Chen;黄宇韬/Yutao Huang | |
| 桂旭/Xu Gui;陈维耀/Weiyao Chen |
Alumni/毕业生
| 科研骨干/Staff | ||
| 2020.12-2024.03 | 杨辉/Hui Yang | 某高等学校教师 |
| 2020.05-2021.12 | 付健/Jian Fu | 某高等学校教师 |
| 2019.10-2021.12 | 曹瑞珉/Ruimin Cao | 某大手通讯终端企业 |
| 学生/ Student | ||
| 2021.09-2023.06 | 宋丰年/Fengnian Song | 某专精特新“小巨人”公司 |
| 实习生/Intern | ||
| 2022.07-2022.08 | 钦壮飞/Zhuangfei Qin | |
| 2021.08-2021.12 | 李嘉驹/Jiaju Li | |
| 2021.08-2021.12 | 林文裕/Wenyu Lin |
1、自动控制原理
2、机器视觉
3、传感器与检测技术
》相关资料下载
| 自动控制原理 | 机器视觉 | 传感器与检测技术 |
 |  |
|
Publications and patents
仅列一作/通讯中代表性论文,https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3261-3728
- Journals (*corresponding author)
Shuangjiang Huang, Fengnian Song, Lihui Wang*, Yutao Huang, Yuan He, Shi Bai, Tao Chen, Masatoshi Ishikawa, High-speed active vision pose perception and tracking method based on Pan-Tilt mirrors for 6-DOF dynamic projection mapping, Optics and Lasers in Engineering, Volume 188, 2025, 108888,[DOI:10.1016/j.optlaseng.2025.108888]
Xianhua Chen, Lihui Wang*, Jianhua Tang, Shuangjiang Huang, Real-time reconstruction of multi-person 3D human pose with perspective transformation matching based on multi-view, Journal of Electronic Imaging, Vol.34(2), pp.023023, (2025) [10.1117/1.JEI.34.2.023023]
Yutao Huang, Lihui Wang*, Shuangjiang Huang, Longfei Fan, Tao Chen, 42 mm large aperture variable-focus lens based on the liquid-membrane-liquid structure, Optics Express, 32(25), pp. 44706-44720 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/OE.539941]
Hui Yang, Tianzhao Bu*, Wenbo Liu, Jiaqi Liu, Yunzhi Ling, Meixia Wu, Weirui Liu, Changan Wang*, Xifeng Gao*, Lihui Wang*, A novel triboelectric-optical hybrid tactile sensor for human-machine tactile interaction, Nano Energy, 125, pp. 109592 (2024) [DOI:10.1016/j.nanoen.2024.109592]
Shuangjiang Huang, Lihui Wang*, Yutao Huang, Yuan He, Shi Bai, Measurement method of virtual image distance for head-mounted display based on a variable-focus liquid lens, Applied Optics, Vol.63, Issue 15, pp. 4175-4181 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/AO.524353]
Huayu Cheng, Lihui Wang*, Satoshi Tabata, Yuan He, Yan Hu, Jiang Liu and Zhiwei Mou, High-speed all-in-focus 3D imaging method based on the liquid lens focus scanning, Applied Optics, Vol.63, Issue 21, pp. 5602-5610 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/AO.523864]
Xiao Zhang, Lihui Wang*, Zhiwei Mou, Yiqi Cao, Yuan He, High-speed eye-tracking based on a synchronized imaging mechanism by dual-ring infrared lighting source, Applied Optics, Vol.63, Issue 16, pp. 4293-4302 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/AO.521840]
Jiaqi Li, Lin Li, Lihui Wang*, Lei Li, Shaoyong Li, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, Adaptive milliseconds tracking and zooming optics based on a high-speed gaze controller and liquid lenses, Optics Express, Vol.32, Issue 2, pp. 2257-2270 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/OE.512003]
Shangen Tang, Lihui Wang*, Fengnian Song, and Shaoyong Li, Dynamic projection mapping for non-planar objects with a variable focus lens and visual feedback, Journal of the Optical Society of America A, Vol. 41, Issue 3, pp. 468-475 (2024) [DOI:10.1364/JOSAA.514287]
王立輝,田畑智志,徐鴻金,胡云普,渡辺義浩,石川正俊:液体レンズを用いた高速焦点追従投影システム, 光学, 53巻, 第6号, p.234 (2024)
Lin Li, Na Xie, Jia-Qi Li, Jing-Yi Fu, Shu-Bin Liu, Li-Hui Wang, Yu-Hai Li, Lei Li, Optofluidic zoom system with increased field of view and less chromatic aberration, Optics Express, Vol.31, Issue 15, pp. 25117-25127 (2023) [DOI:10.1364/OE.498096]
Hui Yang, Jiaqi Liu, Wenbo Liu, Weirui Liu, Zilong Deng, Yunzhi Ling, Changan Wang, Meixia Wu, Lihui Wang* and Li Wen*, Compliant Grasping Control for a Tactile Self-Sensing Soft Gripper, Soft Robotics, (2023) [DOI:10.1089/soro.2022.0221]
Ronghua Hu, Hui Yang, Lihui Wang*, and Longfei Fan, Flexible optical tactile sensor based on a liquid-membrane lens structure, Applied Optics, 62(26), 6952-6960 (2023) [DOI:10.1364/AO.496741
Zenghong Duan, Lihui Wang*, Zhi Li, Jian Fu, Susheng Fu, Boqian Chen, Yuxun Chen, and Yong Zhao, “Dynamic performance of a membrane-based variable focus lens with a large aperture,” Appl. Opt. 62, 4609-4617 (2023)[DOI:10.1364/AO.486278]
Lihui Wang*, Satoshi Tabata, Hongjin Xu, Yunpu Hu, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic depth-of-field projection mapping method based on a variable focus lens and visual feedback, Optics Express, 31(3), pp. 3945-3953 (2023) [DOI:10.1364/OE.478416]
Hao Xu, Satoshi Tabata, Haowen Liang*, Lihui Wang*, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: Accurate Measurement of Virtual Image Distance for Near-Eye Displays Based on Auto-Focusing, Applied Optics, 61, 9093-9098 (2022) [DOI: 10.1364/AO.472931]
Yao Li, Lei Min, John H. Xin, Lihui Wang, Qinghua Wu, Longfei Fan*, Feng Gan, and Hui Yu, High-performance Fibrous Artificial Muscle Based on Reversible Shape Memory UHMWPE, Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 20, 7-17, 2022 [DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.07.045]
Ruimin Cao, Hui Yang, Jianjiang Cui, Lina Hao, and Lihui Wang*, Situation Representation and Strategic Reasoning Method of Hybrid Game System Based on Modified Hybrid Stochastic Timed Petri Net, IEEE Systems Journal, 1-11, 2022 [DOI: 10.1109/JSYST.2022.3189547]
Hui Yang, Wenbo Liu, Jiaqi Liu, Yunzhi Ling, Meixia Wu, Weirui Liu, Lihui Wang*, Liquid Lens-based Optical Tactile Sensor with a Touch-Sensing Separable Structure, Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2200674 (2022) (accepted)
Yuping Wang, Senwei Xie, Lihui Wang*, Hongjin Xu, Satoshi Tabata, Masatoshi Ishikawa. ARSlice: Head-Mounted Display Augmented with Dynamic Tracking and Projection, Journal of Computer Science and Technology 37(3), 666-679 (2022) [DOI: 10.1007/s11390-022-2173-y]
Hui Yang, Jian Fu, Ruimin Cao, Jiaqi Liu and Lihui Wang*, “A Liquid Lens-based Optical Sensor for Tactile Sensing,” Smart Materials and Structures 31(3), 035011 (2022) [DOI: 10.1088/1361-665X/ac4d64]
Ruimin Cao, Jian Fu, Hui Yang, Lihui Wang*, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, “Robust optical axis control of monocular active gazing based on pan-tilt mirrors for high dynamic targets,” Optics Express 29, 40214-40230 (2021) [DOI: 10.1364/OE.439083]
Hongjin Xu, Lihui Wang*, Satoshi Tabata, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, Extended depth-of-field projection method using a high-speed projector with a synchronized oscillating variable-focus lens, Applied Optics, 60(13), pp. 3917-3924 (2021) [DOI: 10.1364/AO.419470]
Zhangxu Pan, Chan Guo, Xianchi Wang, Jiucheng Liu, Ruimin Cao, Yanfen Gong, Jiantai Wang, Ningyang Liu, Zhitao Chen, Lihui Wang, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Zheng Gong, Wafer-Scale Micro-LEDs Transferred onto an Adhesive Film for Planar and Flexible Displays, Advanced Materials Technologies, 2000549 (2020)[DOI: 10.1002/admt.202000549]
Chen Zhang, Jianjiang Cui, Lihui Wang, Hao Wang, Multi-focus Image Fusion and Depth Reconstruction, Journal of Electronic Imaging, 29(3), 033016 (2020) [DOI: 10.1117/1.JEI.29.3.033016]
Ruimin Cao, Lihui Wang, Lina Hao, Wenlin Chen, Junxiang Deng, A Decision-making Framework of Hybrid System based on Modified Hybrid Stochastic Timed Petri Net and Deep Learning, IEEE Systems Journal, 2020. [DOI: 10.1109/JSYST.2020.2983044].
Lihui Wang, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic response of elastomer-based liquid-filled variable focus lens, Sensors, Vol.19, No.21, Article No.4624 pp:1-13 (2019) [DOI:10.3390/s19214624]
Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Solar energy-actuated back and forth optical mechanism, Applied Optics, Vol.58, No.15, pp. E7-E11 (2019) [DOI:10.1364/AO.58.0000E7]
Lihui Wang, Jianjiang Cui, Satoshi Tabata, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Low-cost, readily available 3D microscopy imaging system with variable focus spinner, Optics Express, Vol.26, Issue 23, pp. 30576-30587 (2018).[DOI:10.1364/OE.26.030576]
Lihui Wang, Tomohiko Hayakawa, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dielectric-elastomer-based fabrication method for varifocal microlens array, Optics Express, Vol.25, Issue 25, pp. 31708-31717 (2017)[DOI:10.1364/OE.25.031708]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Paraxial ray solution for liquid-filled variable focus lenses, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Volume 56, Number 12, 122501 (2017)[DOI:10.7567/JJAP.56.122501]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, An improved low-optical-power variable focus lens with a large aperture, Optics Express, Vol.22, Issue 16, pp. 19448-19456 (2014)[DOI:10.1364/OE.22.019448]
Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Variable-focus lens with 30 mm optical aperture based on liquid-membranes-liquid structure, Applied Physics Letters, Vol.102, 131111 (2013)[DOI:10.1063/1.4800603]
崔建江, 王立辉, 陈⼤力, 潘峰, 基于近红外图像质量量评价的静脉图像采集系统, 东北大学学报(自然科学版),2009,30(8):1099-1102.
- Invited Speech
30. Lihui Wang, Research on a High-speed Active Vision Pose Perception Method for Dynamic Projection Mapping, 6th International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Control Engineering (IRCE2023) (Jilin, 2023.08.04) / Invited
31. Lihui Wang, Dynamic Performance of the membrane-based variable focus lens, 12th Applied Optics and Photonics China (AOPC2023) (Beijing, 2023.07.26) / Invited
32. Lihui Wang, Dynamic Projection Mapping with High Speed Vision and a Variable Focus Lens, 2022 Optica Applied Industrial Optics (Ireland, 2022.07.25-27) / Invited
33. Lihui Wang, The 6th International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Control Engineering (IRCE 2023), (Tianjin, 2022.09.25)/ Invited
34. Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Satoshi Tabata, Yunpu Hu, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa. High-Speed Focal Tracking Projection Based on Liquid Lens. In Special Interest Group on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques Conference Emerging Technologies (SIGGRAPH ’20 Emerging Technologies), 2020.08.17, Virtual Event, USA. [DOI: 10.1145/3388534.3408333]
35. Lihui Wang, A large aperture variable focus lens and its application on the next generation of clinical optics, 2015 EMN Optoelectronics Meeting (Beijing, 2015.04.26) / Invited, pp. 195-196
- International Conference and Proceedings
36. Kaihan Xu, Lihui Wang*, Fuqin Deng and Jianle Chen, Research on an Occlusion-Resistant Human Pose Estimation Algorithm, 7th International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Control Engineering (IRCE2024) (Xi’an, 2024.08.09)
37. Xianhua Chen, Lihui Wang*, Qiongyao Wang and Jianhua Tang, 3D Human Pose Estimation and Tracking based on FeedbackMechanism, 7th International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Control Engineering (IRCE2024) (Xi’an, 2024.08.09)
38. Xiao Zhang, Lihui Wang*, Yuan He, Zhiwei Mou, Yiqi Cao, Milliseconds eye-tracking mechanism for high precision medical device, 21st IEEE MDBS-BHE’ Symposium 2023 (HongKong, 2023.12.20) / (Oral)
39. Huayu Cheng, Lihui Wang*, Satoshi Tabata, Yuan He, Yan Hu, Jiang Liu, A novel fundus imaging method based on a liquid lens focus scanning, 21st IEEE MDBS-BHE’ Symposium 2023 (HongKong, 2023.12.20) / (Oral)
40. Jiaqi Li, Lihui Wang*, Shaoyong Li, Lin Li, Lei Li, Active milliseconds zooming and tracking optics based on liquid lenses and a high-speed gaze controller, SPIE/COS Photonics Asia (Beijing, 2023.10.14) / (Oral 12765-4) doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2686749
41. Ronghua Hu, Hui Yang, Lihui Wang*, Longfei Fan, Research on a flexible optical tactile sensor based on a liquid lens structure, SPIE/COS Photonics Asia (Beijing, 2023.10.15) / (Oral 12771-12) doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2686776
42. Xiao Zhang, Lihui Wang*, Yuan He, Zhiwei Mou, Yiqi Cao, High-speed eye tracking based on a synchronized image acquisition mechanism by dual-ring infrared lighting source, SPIE/COS Photonics Asia (Beijing, 2023.10.15) / (Oral 12766-13) doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2686717
43. Huayu Cheng, Lihui Wang*, Yuan He, , High-speed all-in-focus 3D imaging technology based on the liquid lens focus scanning, SPIE/COS Photonics Asia (Beijing, 2023.10.16) / (Oral 12767-11) doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2686779
44. Shangen Tang, Lihui Wang*, Fengnian Song, Shaoyong Li, Dynamic projection mapping for non-planar objects with a variable focal lens, SPIE/COS Photonics Asia (Beijing, 2023.10.16) / (Oral 12767-12) doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2686766
45. Shuangjiang Huang, Lihui Wang*, Yuan He, Shi Bai, Measurement method of virtual image distance for near-eye display based on a variable-focus liquid lens, 12th Applied Optics and Photonics China (AOPC2023) (Beijing, 2023.07.25-26) / (Poster AOPC2023-09-022)
46. Huayu Cheng, Lihui Wang*, Yuan He, Yan Hu, Liu Jiang, High-speed all-in-focus 3D imaging method based on the liquid lens focus scanning, 12th Applied Optics and Photonics China (AOPC2023) (Beijing, 2023.07.25-26) / (Poster AOPC2023-09-020)
47. Xiao Zhang, Lihui Wang*, Yuan He, Zhiwei Mou, Yiqi Cao, High-speed eye tracking mechanism based on a synchronized image acquisition by dual-ring infrared lighting source, 12th Applied Optics and Photonics China (AOPC2023) (Beijing, 2023.07.25-26) / (Poster AOPC2023-09-021)
48. Shangen Tang, Lihui Wang*, Fengnian Song, Shaoyong Li, Dynamic projection mapping for non-planar objects with a variable focus lens, 12th Applied Optics and Photonics China (AOPC2023) (Beijing, 2023.07.25-26) / (Poster AOPC2023-06-007)
49. Jiaqi Li, Lihui Wang*, Lin Li, Shaoyong Li, Active milliseconds zooming and tracking optics based on liquid lenses and high-speed gaze control, 12th Applied Optics and Photonics China (AOPC2023) (Beijing,2023.07.25-26) / (Poster AOPC2023-09-023)
50. Jian Fu, Hui Yang, Ruimin Cao, Lihui Wang*, The Influence of Membrane Thickness on the Dynamic Response of Liquid Lens, Frontiers in Optics 2021 (FiO 2021)(Online Event. 2021.11.02)/ (Poster Session) JTu1A.131
51. Hui Yang, Jian Fu, Ruimin Cao, Lihui Wang*, An Optical Tactile Sensor with Liquid Lens Mechanism, Frontiers in Optics 2021 (FiO 2021)(Online Event. 2021.11.03)/ (Poster Session) JW7A.22
52. Ruimin Cao, Hui Yang, Jian Fu, Lihui Wang*, High-speed optical 3D active sensing method for high-dynamic targets in the large-field scene, Frontiers in Optics 2021 (FiO 2021)(Online Event. 2021.11.03)/ (Poster Session) JW7A.35
53. Lihui Wang, Satoshi Tabata, Hongjin Xu, Yunpu Hu, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa, Interactive Dynamic Extended Depth-of-Field Projection Mapping with Variable Focus Lens and Visual Feedback Control, International Conference on Display Technology 2021, (Beijing, May 31, 2020)
54. Jian Fu, Ruimin Cao, Lihui Wang*, The influence of the apodization function on the optical needle, Frontiers in Optics 2020 (FiO 2020)(Online Event. 2020.09.14-17)/ (Poster Session)
55. Ruimin Cao, Lihui Wang*, Jian Fu, Adaptive self-window-based optical information acquisition method for high dynamic target, Frontiers in Optics 2020 (FiO 2020)(Online Event. 2020.09.16)/ (Oral Session)
56. Lihui Wang, Satoshi Tabata, Hirotoshi Takeuchi, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: A study for accelerating the speed of all-in-focus image processing, SPIE Photonics West 2020 (San Francisco, 2020.2.5)/Proceedings of SPIE Vol. 11245, Three-Dimensional and Multidimensional Microscopy: Image Acquisition and Processing XXVII; 112450U (2020) [DOI: 10.1117/12.2542686]
57. Hongjin Xu, Lihui Wang*, Satoshi Tabata, Yoshihiro Watanabe, and Masatoshi Ishikawa: An extended depth-of-field projection method using a high-speed projector with a synchronized oscillating variable focus lens, SPIE Photonics West 2020 (San Francisco, 2020.2.5)/Proceedings of SPIE Vol.11304 , Advances in Display Technologies X, 113040T (2020) [DOI: 10.1117/12.2542477]
58. Lihui Wang, Yunpu Hu, Hongjin Xu, Masatoshi Ishikawa, A method for passive, monocular distance measurement of virtual image in VR/AR, The IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography 2019 (ICCP 2019) (Tokyo, Japan. 2019.05.15)/ [link]
59. Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Yunpu Hu, Satoshi Tabata, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic Depth-of-Field Projection for 3D Projection Mapping, ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI’19) (Glasgow, Scotland, UK. 2019.05.05-09) [DIO: 10.1145/3290607.3313246]
60. Lihui Wang, Yunpu Hu, Hongjin Xu, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dynamic focal tracker display, SPIE Photonics West 2019 (San Francisco, California, USA. 2019.02.07)/ (Oral Session) [DIO: 10.1117/12.2506958]
61. Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Optical Mechanism controlled by Shape Memory Alloy Spring, 11th International Conference on Optics-Photonics Design and Fabrication (ODF’18, Hiroshima), (Hiroshima, Japan. 2018.11.29)/ (Poster Session) [Paper, 29PSb-36]
62. Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Solar Energy Actuated Optical Mechanism, OSA Light, Energy and the Environment Congress, (Singapore. 2018.11.06)/ (Poster Session) [DIO:10.1364/FTS.2018.JT2A.11]
63. Lihui Wang, Jianjiang Cui, Satoshi Tabata, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Readily Available Varifocal Microscope Imaging System, 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (Honolulu, Hawaii, USA. 2018.07.20)/ (Poster Session) [Paper, FrPoS-31.3]
64. Lihui Wang, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Investigation of the dynamic response performance for the liquid-filled variable focus lens, SPIE Photonics West 2018 (San Francisco, California, USA. 2018.01.31)/ (Poster Session) [DIO:10.1117/12.2288845]
65. Kenichi Murakami, Lihui Wang, Tomohiko Hayakawa, Taku Senoo, Masatoshi Ishikawa: Catching Robot Hand System in Dynamic Depth Variation with a Rotating Variable Focusing Unit, Frontiers in Optics 2017 (FiO 2017)(Washington DC, USA. 2017.9.19)/ (Poster Session) [DIO:10.1364/FIO.2017.JTu2A.52]
66. Lihui Wang, Tomohiko Hayakawa, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Depth of field extended imaging method based on intensification of time and spatial expansion, SPIE Smart Structures/NDE 2017(Portland, Oregon, USA. 2017.03.26)/ (Oral Session) [DIO:10.1117/12.2259891]
67. Lihui Wang, Tomohiko Hayakawa, Masatoshi Ishikawa, A fabrication method for variable focus micro lens array based on deformation of dielectric elastomer actuator, European Optical Society Bi-Annual Meeting (EOSAM) 2016 (Berlin, Germany. 2016.09.28)/ (Oral Session)
68. Tomohiko Hayakawa, Lihui Wang, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Three-dimensional scanning method based on deformation of a dielectric elastomer actuator, European Optical Society Bi-Annual Meeting (EOSAM) 2016 (Berlin, Germany. 2016.09.29)/ (Poster Session)
69. Tomohiko Hayakawa, Lihui Wang, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Dielectric elastomer-based laser beam pointing method with ultraviolet and visible wavelength , SPIE Photonics West 2016 (San Francisco, California, USA. 2016.02.17)/ (Poster Session) [DOI:10.1117/12.2212081]
70. Tomohiko Hayakawa, Lihui Wang, Masatoshi Ishikawa, A Novel Precise Laser Manipulation Method with Dielectric Elastomer, OSA’s 99th annual meeting, Frontiers in Optics 2015 (FiO 2015)(San Jose, California, USA. 2015.10.19)/ (Oral Session) [DOI:10.1364/FIO.2015.FM2G.5]
71. Lihui Wang, Alvaro Cassinelli, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, A pair of diopter adjustable eyeglasses for presbyopia vision correction, SPIE Optics + Photonics 2014 (San Diego, California, USA, 2014.08.18) // Proc. of SPIE, Vol.9193, 91931G-1(Poster Session)[DOI:10.1117/12.2061659]
72. Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Adaptive achromatic doublet design by double variable-focus lenses, SPIE Optics + Photonics 2014 (San Diego, California, USA, 2014.08.17-21) / [(Oral Session)][DOI:10.1117/12.2061203]
73. Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, A Weak Power Enhanced Liquid-Membrane-Liquid Lens by a Pretension Elastic Membrane, OSA’s 97th annual meeting, Frontiers in Optics 2013/ Laser Science XXIX(FiO/LS 2013)(Orlando, Florida, USA, 2013.10.06-10)/ (Oral Session) [OSA Technical Digest FTu5F.5] [DOI: 10.1364/FIO.2013.FTu5F.5]
74. Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, A solution of pre-tension membrane for improving the usability of liquid-membrane-liquid lens in its weak power area, 2nd EOS Conference on Optofluidics 2013 (Munich, Germany, 2013.05.13-15) / (Oral Session)
75. Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, Development of variable-focal lens with liquid-membrane-liquid structure and 30mm optical aperture, SPIE Photonics West 2013 (San Francisco, California, USA, 2013.02.02-07) / (Oral Session) [SPIE Proceedings 8617-5] [DOI:10.1117/12.2005531]
76. Lihui Wang, Hiromasa Oku, Masatoshi Ishikawa, A Liquid Lens with Liquid-Membrane-Liquid Structure, OSA’s 96th annual meeting, Frontiers in Optics 2012/ Laser Science XXVIII(FiO/LS 2012)(Rochester, NewYork, USA, 2012.10.14-18)/ (Oral Session)[OSA Technical Digest FM3A.3][DOI:10.1364/FIO.2012.FM3A.3]
77. Cui Jianjiang, Shi Dayu, Wang Lihui, Chen Dali, Liu Feng, Design and Realization of Route Control System in Railway System Based on Simulation, Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Logistics Systems and Intelligent Management (ICLSIM 2010), 2010: 989-993. [DOI: 10.1109/ICLSIM.2010.5461103(EI Index:11291780)]
78. Cui Jianjiang, Wang Lihui, Sun Lei, Zhang Yaowen, Wang Guoren, A Method of Near-Infrared Image Acquisition Based on Image Quality Assessment, Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Measurement and Control of Granular Materials (MCGM 2009), 2009: 509-512.
- Patents
1. プロジェクタの制御装置、プロジェクタ、投影システム、投影方法及びプログラム、渡辺義浩、王立輝、徐鴻金、東京大学、東京工業大学、PCT/JP2020/034180
(Projector and its control device, system, method, and program, Masatooshi Ishikawa, Yoshihiro Watanabe, Lihui Wang, Hongjin Xu, The University of Tokyo and Tokyo Institute of Technology, PCT/JP2020/034180)
2. 可変焦点レンズ、奥寛雅、王立輝、石川正俊、東京大学、PCT/JP2013/062988
(Variable focus lens, Hiromasa Oku, Lihui Wang, Masatoshi Ishikawa, The University of Tokyo, PCT/JP2013/062988)
3. (已授权)并联式运动目标视觉追踪装置
4. (已授权)三维空间激光投影切片显示装置
5. (已授权)按压式触觉传感器
6. (已授权)叶片追光及摄像装置
7. (已授权)阵列式触觉传感器
8. (已授权)一种光学传感装置、传感设备及系统
9. (审查中)(PCT)一种反射式高速自动追光设备
10. (审查中)动态监控摄像装置和动态监控方法
11. (审查中)视觉防抖装置和方法
12. (审查中)液体透镜运行调控系统、液体透镜运行调控方法及装置
Media and others
1. Dynamic Projection Mapping
1) ITmedia News. 液体レンズを用いた高速焦点追従投影システム[https://dip-labs.com/news/20210128-01/] (2021.01) (日本語)
译:ITmedia News,基于液体的动态光雕投影系统。
2) 中国科技网/科技日报. “液体透镜带来光学镜头革命” [http://www.stdaily.com/index/kejixinwen/2019-11/21/content_817911.shtml?from=singlemessage](2019.11) (in Chinese)
3) 日刊工業新聞. “動く物体に絵を投影できるプロジェクション技術、どんな用途に使う”[https://newswitch.jp/p/20672?fbclid=IwAR3MP-srPICwf7SsFN333tQQ-9pA-Jddmu1eq8ElD61jKqIMw6nge9yeGrU] (2020.01) (in Japanese)
译:日刊工业新闻。可在移动物体表面绘画的光雕投影技术,潜在用途是?
2. Variable Focus Lens
1) テレビ東京ワールドビジネスサテライトトレンドたまご[オートフォーカスの老眼鏡!?] [https://txbiz.tv-tokyo.co.jp/wbs/trend_tamago/post_124134/] (2017.01) (in Japanese)
译:东京电视台,全球财经卫视Trend Tamago专题,自动对焦老花眼眼镜!
3. 3D AR Head-Up-Display for ADAS Automotive
1) Konica Minolta Release. “Konica Minolta Develops the World’s First* Automotive 3D Augmented Reality Head-up Display” [https://www.konicaminolta.com/newsroom/2017/0227_01_01.html]. (2017.02)
2) コニカミノルタニュースリリース.“コニカミノルタ 世界初*の車載用3D 拡張現実ヘッドアップディスプレイを開発” [https://www.konicaminolta.com/jp-ja/newsroom/2017/0113_01_01.html]. (2017.01) (in Japanese)
3) 日本経済新聞. “車載用3D拡張現実ヘッドアップディスプレーを開発” [https://www.nikkei.com/article/DGXLRSP433224_T10C17A1000000/].(2017.01) (in Japanese)
欢迎感兴趣的研究者和同学联系。
wanglihui[at]suda.edu.cn
